Zhipu AI officially released GLM-5 on February 11, 2026. It's currently one of the largest open-source Large Language Models by parameter count. GLM-5 utilizes a 744B MoE (Mixture of Experts) architecture, activating 40B parameters per inference, and has reached the top tier for open-source models in reasoning, coding, and Agent tasks.
Core Value: By the end of this post, you'll understand GLM-5's technical architecture, how to call its API, how to configure Thinking reasoning mode, and how to get the most out of this 744B open-source flagship in your real-world projects.

GLM-5 Core Parameters at a Glance
Before we dive into the technical details, let's look at the key specs for GLM-5:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total Parameters | 744B (744 Billion) | One of the largest open-source models today |
| Active Parameters | 40B (40 Billion) | Actually used during each inference |
| Architecture | MoE (Mixture of Experts) | 256 experts, 8 activated per token |
| Context Window | 200,000 tokens | Supports ultra-long document processing |
| Max Output | 128,000 tokens | Meets long-form generation needs |
| Pre-training Data | 28.5T tokens | 24% increase over the previous generation |
| License | Apache-2.0 | Fully open-source, supports commercial use |
| Training Hardware | Huawei Ascend Chips | Fully domestic compute stack, no reliance on overseas hardware |
A standout feature of GLM-5 is that it's trained entirely on Huawei Ascend chips and the MindSpore framework, fully validating the domestic compute stack. For developers in China, this means another powerful, self-controllable option for their tech stack.
Evolution of the GLM Series
GLM-5 is the fifth generation of Zhipu AI's GLM series, with each generation bringing significant leaps in capability:
| Version | Release Date | Parameter Scale | Core Breakthrough |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-4 | 2024-01 | Undisclosed | Multimodal base capabilities |
| GLM-4.5 | 2025-03 | 355B (32B active) | First introduction of MoE architecture |
| GLM-4.5-X | 2025-06 | Same as above | Enhanced reasoning, flagship positioning |
| GLM-4.7 | 2025-10 | Undisclosed | Thinking reasoning mode |
| GLM-4.7-FlashX | 2025-12 | Undisclosed | Ultra-low cost fast inference |
| GLM-5 | 2026-02 | 744B (40B active) | Agent capability breakthrough, hallucination rate down 56% |
From GLM-4.5's 355B to GLM-5's 744B, the total parameter count has more than doubled. Active parameters increased from 32B to 40B (a 25% jump), and pre-training data grew from 23T to 28.5T tokens. Behind these numbers lies Zhipu AI's massive investment across compute, data, and algorithms.
🚀 Quick Start: GLM-5 is already live on APIYI (apiyi.com). The pricing matches the official site, and with their top-up bonus, you can grab about a 20% discount—perfect for developers looking to dive into this 744B flagship model right away.
GLM-5 MoE Architecture Technical Analysis
Why GLM-5 Chose the MoE Architecture
MoE (Mixture of Experts) is currently the mainstream technical path for scaling Large Language Models. Unlike Dense architectures (where all parameters participate in every inference), the MoE architecture only activates a small subset of expert networks to process each token. This significantly reduces inference costs while maintaining the model's massive knowledge capacity.
The MoE architecture design of GLM-5 features several key characteristics:
| Architectural Feature | GLM-5 Implementation | Technical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total Experts | 256 | Massive knowledge capacity |
| Active per Token | 8 experts | High inference efficiency |
| Sparsity Rate | 5.9% | Uses only a small fraction of parameters |
| Attention Mechanism | DSA + MLA | Lower deployment costs |
| Memory Optimization | MLA reduces usage by 33% | Lower VRAM footprint |
Simply put, although GLM-5 has 744B parameters, it only activates 40B (about 5.9%) during each inference. This means its inference cost is much lower than a Dense model of the same scale, yet it can still leverage the rich knowledge embedded within its 744B parameters.
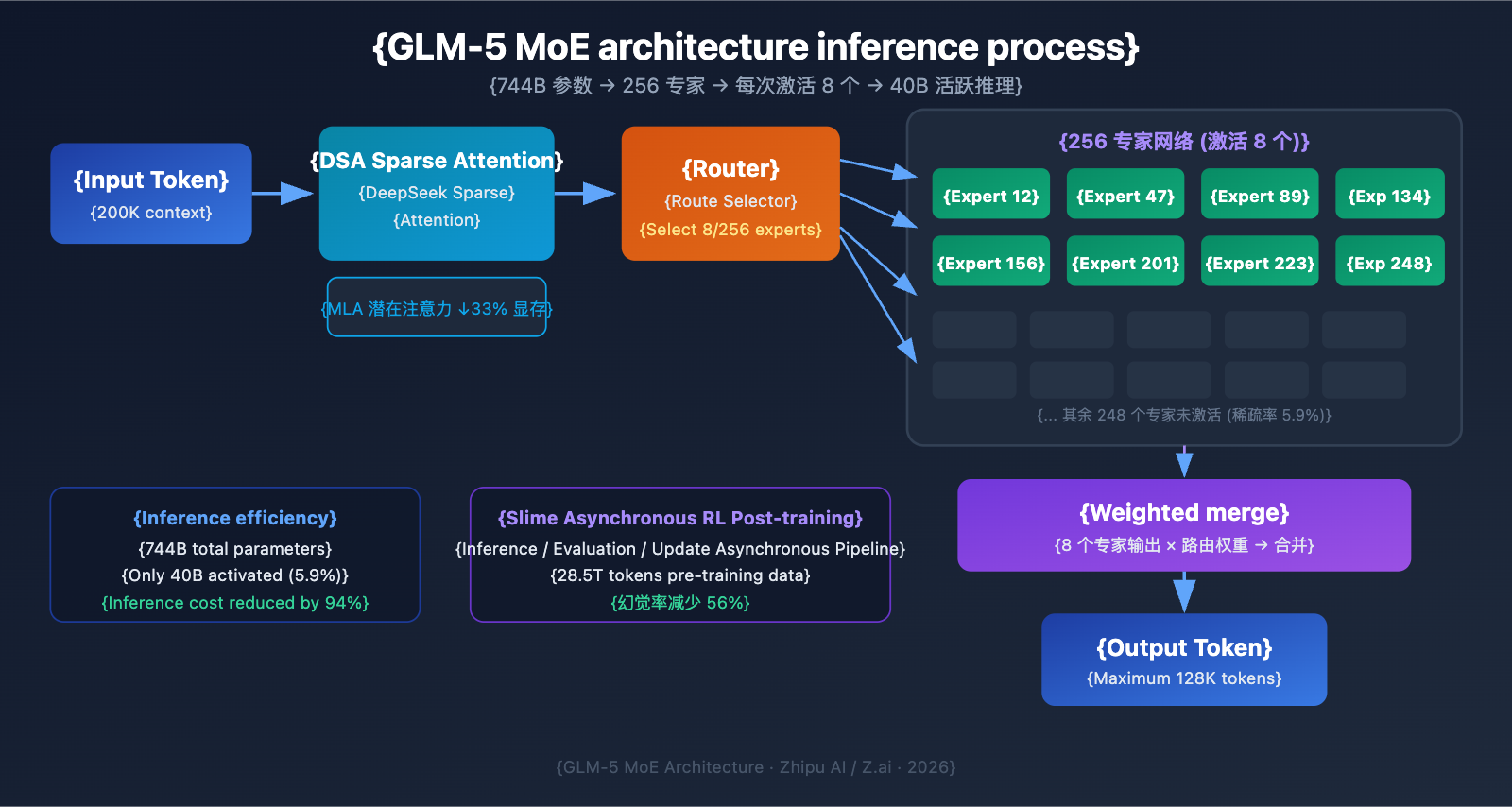
GLM-5's DeepSeek Sparse Attention (DSA)
GLM-5 integrates the DeepSeek Sparse Attention mechanism, a technology that significantly lowers deployment costs while maintaining long-context capabilities. Combined with Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA), GLM-5 operates efficiently even within an ultra-long context window of 200K tokens.
Specifically:
- DSA (DeepSeek Sparse Attention): Reduces the complexity of attention calculations through sparse attention patterns. Traditional full attention mechanisms require massive computation when processing 200K tokens. DSA lowers this overhead by selectively focusing on key token positions while preserving information integrity.
- MLA (Multi-head Latent Attention): Compresses the KV cache of attention heads into a latent space, reducing memory usage by about 33%. In long-context scenarios, the KV cache is typically the primary consumer of VRAM; MLA effectively alleviates this bottleneck.
The combination of these two technologies means that even a 744B scale model can run on just 8 GPUs using FP8 quantization, drastically lowering the barrier to deployment.
GLM-5 Post-training: The Slime Asynchronous RL System
GLM-5 utilizes a new asynchronous reinforcement learning infrastructure called "Slime" for post-training. Traditional RL training suffers from efficiency bottlenecks—there's a lot of waiting time between generation, evaluation, and update steps. Slime makes these steps asynchronous, enabling finer-grained post-training iterations and significantly boosting training throughput.
In a traditional RL training workflow, the model must complete a batch of inferences, wait for evaluation results, and then update parameters—executing these three steps serially. Slime decouples these into independent asynchronous pipelines, allowing inference, evaluation, and updates to happen in parallel.
This technical improvement is directly reflected in GLM-5's hallucination rate, which has decreased by 56% compared to the previous generation. More thorough post-training iterations have allowed the model to achieve noticeable improvements in factual accuracy.
GLM-5 vs. Dense Architecture
To better understand the advantages of the MoE architecture, we can compare GLM-5 with a hypothetical Dense model of the same scale:
| Dimension | GLM-5 (744B MoE) | Hypothetical 744B Dense | Actual Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters per Inference | 40B (5.9%) | 744B (100%) | MoE reduced by 94% |
| Inference VRAM Requirement | 8x GPU (FP8) | ~96x GPU | MoE is significantly lower |
| Inference Speed | Fast | Extremely slow | MoE is better for deployment |
| Knowledge Capacity | Full 744B knowledge | Full 744B knowledge | Equivalent |
| Specialization | Experts excel at different tasks | Unified processing | MoE is more refined |
| Training Cost | High but manageable | Extremely high | MoE offers better ROI |
The core advantage of the MoE architecture is that it provides the knowledge capacity of 744B parameters while maintaining the high efficiency of a 40B parameter inference cost. This is why GLM-5 can deliver cutting-edge performance while offering pricing far lower than comparable closed-source models.
GLM-5 API Quick Start
GLM-5 API Request Parameters Explained
Before you start coding, let's take a look at the GLM-5 API parameter configuration:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
model |
string | ✅ | – | Fixed as "glm-5" |
messages |
array | ✅ | – | Standard chat format messages |
max_tokens |
int | ❌ | 4096 | Maximum output tokens (upper limit 128K) |
temperature |
float | ❌ | 1.0 | Sampling temperature; lower is more deterministic |
top_p |
float | ❌ | 1.0 | Nucleus sampling parameter |
stream |
bool | ❌ | false | Whether to use streaming output |
thinking |
object | ❌ | disabled | {"type": "enabled"} to enable reasoning |
tools |
array | ❌ | – | Function Calling tool definitions |
tool_choice |
string | ❌ | auto | Tool selection strategy |
GLM-5 Minimalist Calling Example
GLM-5 is compatible with the OpenAI SDK interface format. You can quickly integrate it by just swapping the base_url and model parameters:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1" # APIYI统一接口
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-5",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一位资深的 AI 技术专家"},
{"role": "user", "content": "解释 MoE 混合专家架构的工作原理和优势"}
],
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=4096
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
The code above shows the most basic way to call GLM-5. The model ID is glm-5, and the interface is fully compatible with OpenAI's chat.completions format. Migrating existing projects only requires changing two parameters.
GLM-5 Thinking Reasoning Mode
GLM-5 supports "Thinking" reasoning mode, similar to the extended reasoning capabilities found in DeepSeek R1 and Claude. Once enabled, the model performs internal chain-of-thought reasoning before answering, significantly boosting performance on complex math, logic, and programming problems:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1" # APIYI统一接口
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-5",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "证明: 对于所有正整数 n, n^3 - n 能被 6 整除"}
],
extra_body={
"thinking": {"type": "enabled"}
},
temperature=1.0 # Thinking 模式建议使用 1.0
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Recommendations for GLM-5 Thinking Mode:
| Scenario | Enable Thinking? | Suggested Temperature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Math Proofs/Competitions | ✅ Yes | 1.0 | Requires deep reasoning |
| Code Debugging/Architecture | ✅ Yes | 1.0 | Requires systematic analysis |
| Logical Reasoning/Analysis | ✅ Yes | 1.0 | Requires chain-of-thought |
| Daily Chat/Writing | ❌ No | 0.5-0.7 | Complex reasoning not needed |
| Info Extraction/Summary | ❌ No | 0.3-0.5 | Best for stable output |
| Creative Content Generation | ❌ No | 0.8-1.0 | Needs diversity |
GLM-5 Streaming Output
For scenarios requiring real-time interaction, GLM-5 supports streaming output, allowing users to see results as the model generates them:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1"
)
stream = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-5",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "用 Python 实现一个带缓存的 HTTP 客户端"}
],
stream=True,
temperature=0.6
)
for chunk in stream:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content, end="", flush=True)
GLM-5 Function Calling and Agent Building
GLM-5 natively supports Function Calling, which is the core capability for building AI Agent systems. GLM-5 scored 50.4% on HLE w/ Tools, surpassing Claude Opus (43.4%), demonstrating its excellence in tool invocation and task orchestration:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1"
)
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_documents",
"description": "搜索知识库中的相关文档",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "搜索关键词"},
"top_k": {"type": "integer", "description": "返回结果数量", "default": 5}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "execute_code",
"description": "在沙箱环境中执行 Python 代码",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"code": {"type": "string", "description": "要执行的 Python 代码"},
"timeout": {"type": "integer", "description": "超时时间(秒)", "default": 30}
},
"required": ["code"]
}
}
}
]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-5",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个能够搜索文档和执行代码的AI助手"},
{"role": "user", "content": "帮我查一下 GLM-5 的技术参数,然后用代码画一个性能对比图"}
],
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
# 处理工具调用
message = response.choices[0].message
if message.tool_calls:
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
print(f"调用工具: {tool_call.function.name}")
print(f"参数: {tool_call.function.arguments}")
View cURL Example
curl https://api.apiyi.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "glm-5",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一位资深软件工程师"},
{"role": "user", "content": "设计一个分布式任务调度系统的架构"}
],
"max_tokens": 8192,
"temperature": 0.7,
"stream": true
}'
🎯 Technical Tip: GLM-5 is compatible with the OpenAI SDK format. You can migrate existing projects by simply updating the
base_urlandmodelparameters. By calling it through the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform, you can enjoy unified interface management and top-up bonus offers.
GLM-5 Benchmark Performance Testing
GLM-5 Core Benchmark Data
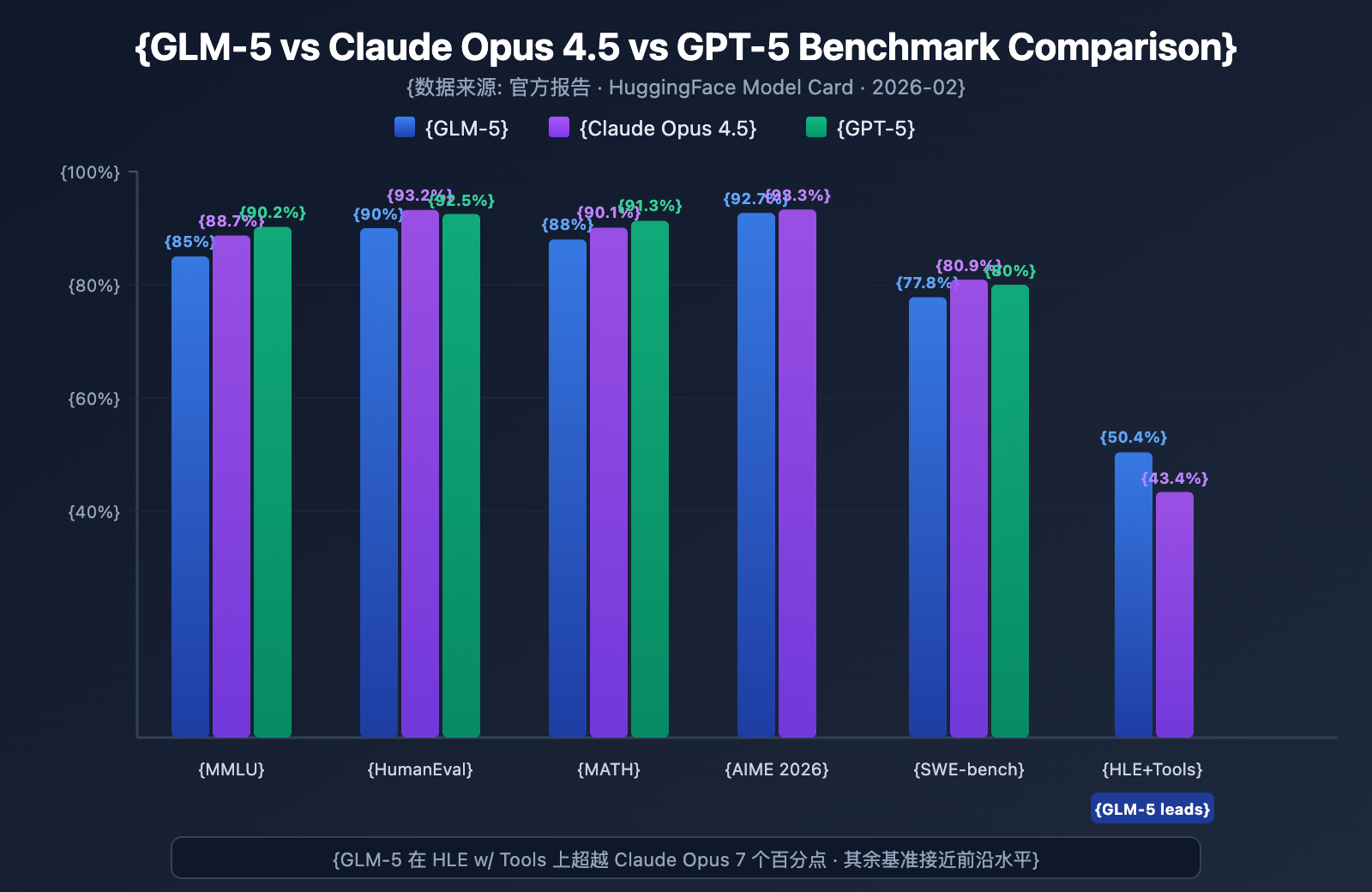
GLM-5 has demonstrated top-tier performance among open-source models across several mainstream benchmarks:
| Benchmark | GLM-5 | Claude Opus 4.5 | GPT-5 | Test Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMLU | 85.0% | 88.7% | 90.2% | 57 Subject Knowledge |
| MMLU Pro | 70.4% | – | – | Enhanced Multi-subject |
| GPQA | 68.2% | 71.4% | 73.1% | Graduate-level Science |
| HumanEval | 90.0% | 93.2% | 92.5% | Python Programming |
| MATH | 88.0% | 90.1% | 91.3% | Math Reasoning |
| GSM8k | 97.0% | 98.2% | 98.5% | Math Word Problems |
| AIME 2026 I | 92.7% | 93.3% | – | Math Competition |
| SWE-bench | 77.8% | 80.9% | 80.0% | Real Software Engineering |
| HLE w/ Tools | 50.4% | 43.4% | – | Reasoning with Tools |
| IFEval | 88.0% | – | – | Instruction Following |
| Terminal-Bench | 56.2% | 57.9% | – | Terminal Operations |
GLM-5 Performance Analysis: 4 Core Advantages
The benchmark data highlights several noteworthy points:
1. GLM-5 Agent Capabilities: HLE w/ Tools Surpasses Closed-Source Models
GLM-5 achieved a score of 50.4% on Humanity's Last Exam (with tool use), surpassing Claude Opus's 43.4% and trailing only Kimi K2.5's 51.8%. This indicates that in Agent scenarios—complex tasks requiring planning, tool invocation, and iterative problem-solving—GLM-5 has reached the level of frontier models.
This result aligns with GLM-5's design philosophy: it has been specifically optimized for Agent workflows from its architecture to post-training. For developers looking to build AI Agent systems, GLM-5 offers an open-source, high-performance, and cost-effective choice.
2. GLM-5 Coding Ability: Entering the First Tier
With 90% on HumanEval and 77.8% on SWE-bench Verified, GLM-5's performance in code generation and real-world software engineering tasks is very close to Claude Opus (80.9%) and GPT-5 (80.0%). For an open-source model, 77.8% on SWE-bench is a major breakthrough—it means GLM-5 can understand real GitHub issues, locate code problems, and submit valid fixes.
3. GLM-5 Mathematical Reasoning: Approaching the Ceiling
On AIME 2026 I, GLM-5 scored 92.7%, trailing Claude Opus by only 0.6 percentage points. A 97% score on GSM8k also shows that GLM-5 is highly reliable for medium-difficulty math problems. Its MATH score of 88% similarly places it in the top tier.
4. GLM-5 Hallucination Control: Drastically Reduced
According to official data, GLM-5 has reduced its hallucination rate by 56% compared to previous versions. This is thanks to more thorough post-training iterations powered by the Slime asynchronous RL system. In scenarios requiring high accuracy, such as information extraction, document summarization, and knowledge base Q&A, lower hallucination rates translate directly into more reliable output.
Positioning GLM-5 Among Peer Open-Source Models
In the current competitive landscape of open-source Large Language Models, GLM-5's positioning is clear:
| Model | Parameter Scale | Architecture | Core Advantages | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-5 | 744B (40B active) | MoE | Agent + Low Hallucination | Apache-2.0 |
| DeepSeek V3 | 671B (37B active) | MoE | Cost-performance + Reasoning | MIT |
| Llama 4 Maverick | 400B (17B active) | MoE | Multimodal + Ecosystem | Llama License |
| Qwen 3 | 235B | Dense | Multilingual + Tools | Apache-2.0 |
GLM-5's competitive edge is mainly reflected in three areas: specialized optimization for Agent workflows (leading in HLE w/ Tools), extremely low hallucination rates (56% reduction), and supply chain security provided by training on domestic computing power. For enterprises needing to deploy frontier open-source models locally, GLM-5 is an option that deserves serious attention.
GLM-5 Pricing and Cost Analysis
GLM-5 Official Pricing
| Billing Type | Z.ai Official Price | OpenRouter Price | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Token | $1.00/M | $0.80/M | Per million input tokens |
| Output Token | $3.20/M | $2.56/M | Per million output tokens |
| Cached Input | $0.20/M | $0.16/M | Input price on cache hit |
| Cache Storage | Temporarily free | – | Cache data storage fee |
GLM-5 vs. Competitor Pricing Comparison
GLM-5's pricing strategy is highly competitive, especially when compared to closed-source flagship models:
| Model | Input ($/M) | Output ($/M) | Cost Relative to GLM-5 | Model Positioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-5 | $1.00 | $3.20 | Benchmark | Open-source Flagship |
| Claude Opus 4.6 | $5.00 | $25.00 | ~5-8x | Closed-source Flagship |
| GPT-5 | $1.25 | $10.00 | ~1.3-3x | Closed-source Flagship |
| DeepSeek V3 | $0.27 | $1.10 | ~0.3x | Open-source Value |
| GLM-4.7 | $0.60 | $2.20 | ~0.6-0.7x | Previous Gen Flagship |
| GLM-4.7-FlashX | $0.07 | $0.40 | ~0.07-0.13x | Ultra-low Cost |
Price-wise, GLM-5 sits right between GPT-5 and DeepSeek V3—it's significantly cheaper than most closed-source flagships, but slightly pricier than lightweight open-source models. Given its 744B parameter scale and top-tier open-source performance, this pricing is quite reasonable.
GLM Full Product Line and Pricing
If GLM-5 doesn't perfectly fit your specific use case, Zhipu also offers a complete product line to choose from:
| Model | Input ($/M) | Output ($/M) | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-5 | $1.00 | $3.20 | Complex reasoning, Agents, long documents |
| GLM-5-Code | $1.20 | $5.00 | Dedicated to code development |
| GLM-4.7 | $0.60 | $2.20 | Medium-complexity general tasks |
| GLM-4.7-FlashX | $0.07 | $0.40 | High-frequency, low-cost calls |
| GLM-4.5-Air | $0.20 | $1.10 | Lightweight & balanced |
| GLM-4.7/4.5-Flash | Free | Free | Entry-level experience and simple tasks |
💰 Cost Optimization: GLM-5 is now live on APIYI (apiyi.com), with pricing identical to Z.ai's official rates. Through the platform's top-up bonus promotions, your actual usage cost can drop to about 80% of the official price—perfect for teams and developers with consistent API needs.
GLM-5 Use Cases and Selection Advice
Which Scenarios Suit GLM-5 Best?
Based on GLM-5's technical features and benchmark performance, here are some specific recommendations:
Highly Recommended Scenarios:
- Agent Workflows: GLM-5 is specifically designed for long-cycle Agent tasks. Its HLE w/ Tools score of 50.4% surpasses Claude Opus, making it ideal for building Agent systems that require autonomous planning and tool calling.
- Software Engineering Tasks: With 90% on HumanEval and 77.8% on SWE-bench, it's more than capable of code generation, bug fixing, code reviews, and architectural design.
- Math and Scientific Reasoning: Scoring 92.7% on AIME and 88% on MATH, it's well-suited for mathematical proofs, formula derivation, and scientific computing.
- Ultra-long Document Analysis: Its 200K context window allows it to handle entire codebases, technical manuals, legal contracts, and other massive texts.
- Low-hallucination Q&A: With a 56% reduction in hallucination rates, it's perfect for knowledge base Q&A, document summarization, and scenarios requiring high accuracy.
Scenarios Where Other Options Might Be Better:
- Multimodal Tasks: The core GLM-5 model only supports text. If you need image understanding, go with a vision model like GLM-4.6V.
- Extreme Low Latency: A 744B MoE model won't be as fast as smaller models. For high-frequency, low-latency needs, GLM-4.7-FlashX is a better bet.
- Ultra-low-cost Batch Processing: If you're processing massive amounts of text where quality isn't the absolute priority, DeepSeek V3 or GLM-4.7-FlashX will be more cost-effective.
GLM-5 vs. GLM-4.7 Selection Comparison
| Comparison Dimension | GLM-5 | GLM-4.7 | Selection Advice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Scale | 744B (40B Active) | Undisclosed | GLM-5 is larger |
| Reasoning Ability | AIME 92.7% | ~85% | Choose GLM-5 for complex reasoning |
| Agent Capability | HLE w/ Tools 50.4% | ~38% | Choose GLM-5 for Agent tasks |
| Coding Capability | HumanEval 90% | ~85% | Choose GLM-5 for code development |
| Hallucination Control | 56% Reduction | Baseline | Choose GLM-5 for high accuracy |
| Input Price | $1.00/M | $0.60/M | Choose GLM-4.7 if cost-sensitive |
| Output Price | $3.20/M | $2.20/M | Choose GLM-4.7 if cost-sensitive |
| Context Length | 200K | 128K+ | Choose GLM-5 for long documents |
💡 Selection Tip: If your project requires top-tier reasoning, Agent workflows, or ultra-long context handling, GLM-5 is the way to go. If you're on a tight budget and the task complexity is moderate, GLM-4.7 remains a great cost-effective alternative. Both models are available via the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform, making it easy to switch and test whenever you need.
GLM-5 API FAQ
Q1: What’s the difference between GLM-5 and GLM-5-Code?
GLM-5 is the general flagship model (Input $1.00/M, Output $3.20/M), perfect for all kinds of text tasks. GLM-5-Code is a code-specific enhanced version (Input $1.20/M, Output $5.00/M) that's been extra-optimized for code generation, debugging, and engineering tasks. If your main use case is software development, GLM-5-Code is definitely worth a try. Both models support calls via a unified OpenAI-compatible interface.
Q2: Does GLM-5’s Thinking mode affect output speed?
Yes, it does. In Thinking mode, GLM-5 generates an internal reasoning chain before providing the final answer, so the Time to First Token (TTFT) will increase. For simple questions, we recommend turning off Thinking mode for faster responses. For complex math, programming, and logic problems, it's better to keep it on—it's a bit slower, but the accuracy is significantly higher.
Q3: What code changes are needed to migrate from GPT-4 or Claude to GLM-5?
Migration is super simple; you only need to modify two parameters:
- Change
base_urlto the APIYI interface address:https://api.apiyi.com/v1 - Change the
modelparameter to"glm-5"
GLM-5 is fully compatible with the OpenAI SDK's chat.completions interface format, including system/user/assistant roles, streaming output, Function Calling, and more. Using a unified API proxy platform also lets you switch between models from different providers under the same API Key, which is very convenient for A/B testing.
Q4: Does GLM-5 support image input?
No, it doesn't. GLM-5 itself is a pure text model and doesn't support image, audio, or video input. If you need image understanding capabilities, you can use Zhipu's vision variant models like GLM-4.6V or GLM-4.5V.
Q5: How do I use GLM-5’s Context Caching feature?
GLM-5 supports Context Caching, where the price for cached input is only $0.20/M—just 1/5th the price of normal input. In long conversations or scenarios where you need to repeatedly process the same prefix, the caching feature can significantly reduce costs. Cache storage is currently free. In multi-turn conversations, the system will automatically identify and cache repeated context prefixes.
Q6: What’s the maximum output length for GLM-5?
GLM-5 supports a maximum output length of 128,000 tokens. For most scenarios, the default 4,096 tokens is plenty. If you need to generate long-form text (like full technical documentation or large blocks of code), you can adjust this via the max_tokens parameter. Just keep in mind that the longer the output, the higher the token consumption and the longer you'll have to wait.
GLM-5 API Best Practices
When using GLM-5 in practice, these tips can help you get better results:
GLM-5 System Prompt Optimization
GLM-5 responds very well to system prompts. Designing a solid system prompt can significantly boost output quality:
# Recommended: Clear role definition + output format requirements
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": """You are a senior distributed systems architect.
Please follow these rules:
1. Responses must be structured using Markdown format.
2. Provide specific technical solutions rather than generalities.
3. If code is involved, provide runnable examples.
4. Mark potential risks and notes in appropriate places."""
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Design a message queue system that supports millions of concurrent connections."
}
]
GLM-5 Temperature Tuning Guide
Different tasks have different sensitivities to temperature. Here are some suggestions based on real-world testing:
- temperature 0.1-0.3: For tasks requiring precise output like code generation, data extraction, or format conversion.
- temperature 0.5-0.7: For technical documentation, Q&A, and summaries where you need stability with some expressive flexibility.
- temperature 0.8-1.0: For tasks requiring diversity like creative writing or brainstorming.
- temperature 1.0 (Thinking mode): For deep reasoning tasks like mathematical proofs or complex programming.
GLM-5 Long Context Handling Tips
GLM-5 supports a 200K token context window, but keep these points in mind during use:
- Put important info first: Place the most critical context at the beginning of the prompt rather than the end.
- Segment processing: For documents exceeding 100K tokens, we recommend processing them in segments and then merging them for more stable output.
- Leverage caching: In multi-turn dialogues, identical prefix content is automatically cached, and cached input costs only $0.20/M.
- Control output length: When using long context inputs, set
max_tokensappropriately to avoid unnecessarily long outputs that increase costs.
GLM-5 Local Deployment Reference
If you're looking to deploy GLM-5 on your own infrastructure, here are the primary ways to get it running:
| Deployment Method | Recommended Hardware | Precision | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 8x A100/H100 | FP8 | Mainstream inference framework, supports speculative decoding |
| SGLang | 8x H100/B200 | FP8 | High-performance inference, optimized for Blackwell GPUs |
| xLLM | Huawei Ascend NPU | BF16/FP8 | Adapted for domestic compute stacks |
| KTransformers | Consumer GPUs | Quantized | GPU-accelerated inference |
| Ollama | Consumer hardware | Quantized | The simplest local experience |
GLM-5 provides both BF16 full precision and FP8 quantized weight formats, which you can download from HuggingFace (huggingface.co/zai-org/GLM-5) or ModelScope. The FP8 quantized version significantly reduces VRAM requirements while maintaining most of the performance.
Key configurations needed for deploying GLM-5:
- Tensor Parallelism: 8-way (
tensor-parallel-size 8) - GPU Memory Utilization: Recommended to set at 0.85
- Tool Call Parser:
glm47 - Inference Parser:
glm45 - Speculative Decoding: Supports both MTP and EAGLE methods
For most developers, calling the API is the most efficient route. It saves you the headache of deployment and maintenance costs, letting you focus entirely on building your app. If you have a specific need for private deployment, check out the official docs:
github.com/zai-org/GLM-5
GLM-5 API Call Summary
GLM-5 Core Capabilities at a Glance
| Capability | GLM-5 Performance | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Reasoning | AIME 92.7%, MATH 88% | Math proofs, scientific reasoning, logic analysis |
| Coding | HumanEval 90%, SWE-bench 77.8% | Code generation, bug fixing, architecture design |
| Agent | HLE w/ Tools 50.4% | Tool calling, task planning, autonomous execution |
| Knowledge | MMLU 85%, GPQA 68.2% | Subject Q&A, tech consulting, knowledge extraction |
| Instruction | IFEval 88% | Formatted output, structured generation, rule following |
| Accuracy | Hallucinations reduced by 56% | Document summaries, fact-checking, info extraction |
The Value of the GLM-5 Open Source Ecosystem
GLM-5 is open-sourced under the Apache-2.0 license, which means:
- Commercial Freedom: Enterprises can use, modify, and distribute it for free without paying licensing fees.
- Custom Fine-tuning: You can perform domain-specific fine-tuning on GLM-5 to build industry-specific models.
- Private Deployment: Keep sensitive data within your internal network to meet compliance requirements for finance, healthcare, or government sectors.
- Community Ecosystem: There are already 11+ quantized variants and 7+ fine-tuned versions on HuggingFace, with the ecosystem continuing to expand.
As Zhipu AI's latest flagship model, GLM-5 sets a new benchmark in the open-source Large Language Model space:
- 744B MoE Architecture: A 256-expert system that activates 40B parameters per inference, striking an excellent balance between model capacity and inference efficiency.
- Strongest Open Source Agent: With an HLE w/ Tools score of 50.4%, it outperforms Claude Opus and is specifically designed for long-cycle Agent workflows.
- Trained on Domestic Compute: Built using 100,000 Huawei Ascend chips, proving the cutting-edge model training capabilities of domestic compute stacks.
- High Cost-Efficiency: At $1/M tokens for input and $3.2/M for output, it's priced significantly lower than comparable closed-source models, and the open-source community is free to deploy and fine-tune it.
- 200K Ultra-Long Context: Supports processing entire codebases and massive technical documents in one go, with a maximum output of 128K tokens.
- 56% Lower Hallucination: Slime asynchronous RL post-training has drastically improved factual accuracy.
We recommend using APIYI (apiyi.com) to quickly test out GLM-5's capabilities. The platform's pricing matches the official rates, and with their top-up bonus promotions, you can effectively get about a 20% discount.
This article was written by the APIYI technical team. For more AI model tutorials, please visit the APIYI (apiyi.com) Help Center.