Author's Note: An in-depth comparison of MiniMax-M2.5 and GLM-5, two major open-source models released in February 2026. We'll analyze their strengths across six dimensions: coding, reasoning, agents, speed, pricing, and architecture.
On February 11-12, 2026, two Chinese AI giants released their flagship models almost simultaneously: Zhipu GLM-5 (744B parameters) and MiniMax-M2.5 (230B parameters). Both utilize the MoE architecture and are released under the MIT license, but they've carved out very different niches in terms of capabilities.
Core Value: By the end of this article, you'll clearly understand why GLM-5 excels at reasoning and factual reliability, while MiniMax-M2.5 shines in coding and agent tool-calling. This will help you make the best choice for your specific use case.

MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5: Core Differences Overview
| Comparison Dimension | MiniMax-M2.5 | GLM-5 | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| SWE-Bench Coding | 80.2% | 77.8% | M2.5 leads by 2.4% |
| AIME Math Reasoning | — | 92.7% | GLM-5 excels |
| BFCL Tool Calling | 76.8% | — | M2.5 excels |
| BrowseComp Search | 76.3% | 75.9% | Roughly equal |
| Output Price/1M tokens | $1.20 | $3.20 | M2.5 is 2.7x cheaper |
| Output Speed | 50-100 TPS | ~66 TPS | M2.5 Lightning is faster |
| Total Parameters | 230B | 744B | GLM-5 is larger |
| Active Parameters | 10B | 40B | M2.5 is more lightweight |
MiniMax-M2.5's Core Strengths: Coding and Agents
MiniMax-M2.5 delivers an outstanding performance on coding benchmarks. Its SWE-Bench Verified score of 80.2% not only beats GLM-5's 77.8% but also surpasses GPT-5.2's 80.0%, trailing only slightly behind Claude Opus 4.6 at 80.8%. It scored 51.3% in Multi-SWE-Bench (which tests multi-file collaboration) and reached an impressive 76.8% in the BFCL Multi-Turn tool-calling benchmark.
Thanks to its MoE architecture, M2.5 only activates 10B parameters (just 4.3% of its 230B total), making it the most "lightweight" choice among Tier 1 models with extremely high inference efficiency. The Lightning version can hit 100 TPS, making it one of the fastest frontier models currently available.
GLM-5's Core Strengths: Reasoning and Knowledge Reliability
GLM-5 holds a significant advantage in reasoning and knowledge-based tasks. It achieved a 92.7% in AIME 2026 math reasoning, 86.0% in GPQA-Diamond scientific reasoning, and a score of 50.4 on Humanity's Last Exam (with tools)—outperforming Claude Opus 4.5's 43.4.
GLM-5's most standout capability is its knowledge reliability. It achieved industry-leading results in the AA-Omniscience hallucination evaluation, a 35-point improvement over its predecessor. For scenarios requiring high-precision factual output—such as technical documentation, academic research assistance, or knowledge base construction—GLM-5 is the more reliable choice. Furthermore, its 744B parameters and 28.5 trillion tokens of training data give it a much deeper knowledge reserve.
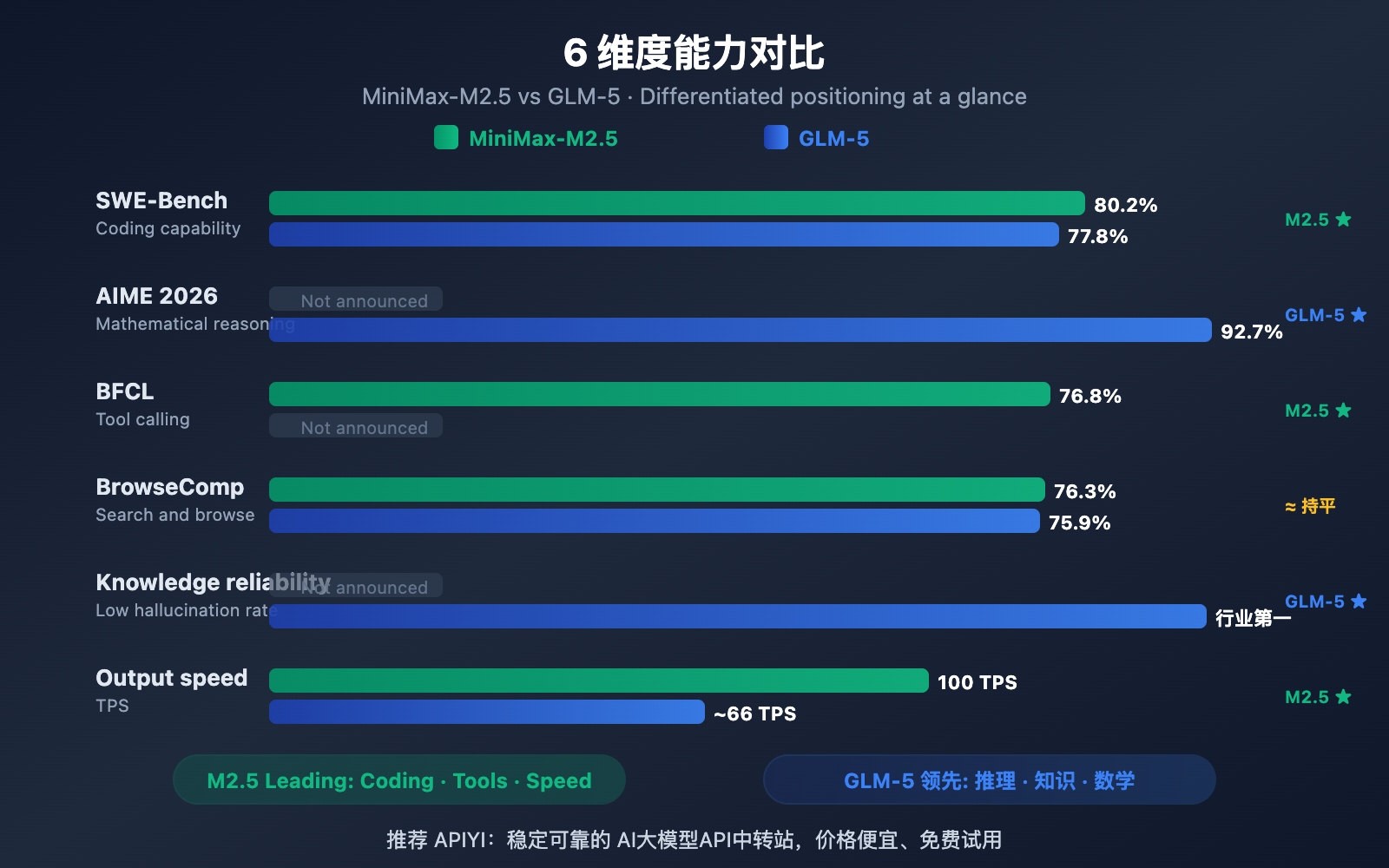
MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5: Detailed Coding Capability Comparison
Coding capability is one of the most critical dimensions developers consider when choosing a Large Language Model. There's a clear gap between these two models in this area.
| Coding Benchmark | MiniMax-M2.5 | GLM-5 | Claude Opus 4.6 (Ref) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SWE-Bench Verified | 80.2% | 77.8% | 80.8% |
| Multi-SWE-Bench | 51.3% | — | 50.3% |
| SWE-Bench Multilingual | — | 73.3% | 77.5% |
| Terminal-Bench 2.0 | — | 56.2% | 65.4% |
| BFCL Multi-Turn | 76.8% | — | 63.3% |
MiniMax-M2.5 leads GLM-5 by 2.4 percentage points on SWE-Bench Verified (80.2% vs 77.8%). In coding benchmarks, this is a significant difference—M2.5's coding capability is at the Opus 4.6 level, while GLM-5 is closer to the Gemini 3 Pro level.
GLM-5 does show its versatility with data for multilingual coding (SWE-Bench Multilingual 73.3%) and terminal environment coding (Terminal-Bench 56.2%). However, on the most core metric, SWE-Bench Verified, M2.5 has a clear edge.
M2.5 also stands out in coding efficiency: it completes a single SWE-Bench task in just 22.8 minutes, a 37% improvement over the previous M2.1. This is thanks to its unique "Spec-writing" coding style—breaking down the architecture first before implementing efficiently, which reduces ineffective trial-and-error loops.
🎯 Coding Scenario Recommendation: If your core need is AI-assisted coding (bug fixes, code reviews, feature implementation), MiniMax-M2.5 is the better choice. You can access both models for side-by-side testing through APIYI (apiyi.com).
MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5: Detailed Reasoning Capability Comparison
Reasoning capability is where GLM-5's core strength lies, especially in math and science reasoning fields.
| Reasoning Benchmark | MiniMax-M2.5 | GLM-5 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIME 2026 | — | 92.7% | Olympic-level math reasoning |
| GPQA-Diamond | — | 86.0% | PhD-level science reasoning |
| Humanity's Last Exam (w/tools) | — | 50.4 | Surpasses Opus 4.5's 43.4 |
| HMMT Nov. 2025 | — | 96.9% | Close to GPT-5.2's 97.1% |
| τ²-Bench | — | 89.7% | Telecom domain reasoning |
| AA-Omniscience Knowledge Reliability | — | Industry Leading | Lowest hallucination rate |
GLM-5 utilizes a new training method called SLIME (Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning Infrastructure), which significantly boosts post-training efficiency. This has allowed GLM-5 to achieve a quantum leap in reasoning tasks:
- AIME 2026 score of 92.7%, close to Claude Opus 4.5's 93.3%, and far exceeding the GLM-4.5 era.
- GPQA-Diamond at 86.0% for PhD-level science reasoning, approaching Opus 4.5's 87.0%.
- Humanity's Last Exam score of 50.4 (with tools), surpassing Opus 4.5's 43.4 and GPT-5.2's 45.5.
GLM-5's most unique trait is its knowledge reliability. In the AA-Omniscience hallucination evaluation, GLM-5 improved by 35 points over its predecessor, reaching industry-leading levels. This means GLM-5 "makes things up" much less often when answering factual questions, which is incredibly valuable for scenarios requiring high-precision information.
MiniMax-M2.5 has less public data regarding reasoning; its core reinforcement learning training is focused on coding and agent scenarios. M2.5's Forge RL framework emphasizes task decomposition and tool-calling optimization across 200,000+ real-world environments, rather than pure reasoning capability.
Comparison Summary: If your core needs involve math reasoning, scientific analysis, or high-reliability knowledge Q&A, GLM-5 has the advantage. We recommend using the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform to test how both perform on your specific reasoning tasks.
MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5: Agent and Search Capabilities

| Agent Benchmark | MiniMax-M2.5 | GLM-5 | Leader |
|---|---|---|---|
| BFCL Multi-Turn | 76.8% | — | M2.5 (Tool Calling) |
| BrowseComp (w/context) | 76.3% | 75.9% | Roughly equal |
| MCP Atlas | — | 67.8% | GLM-5 (Multi-tool coordination) |
| Vending Bench 2 | — | $4,432 | GLM-5 (Long-term planning) |
| τ²-Bench | — | 89.7% | GLM-5 (Domain reasoning) |
The two models show distinct differences in their Agent capabilities:
MiniMax-M2.5 excels as an "Execution-oriented" Agent: It performs exceptionally well in scenarios requiring frequent tool calls, rapid iteration, and efficient execution. A BFCL score of 76.8% means M2.5 can precisely handle function calls, file operations, and API interactions, with tool-calling rounds reduced by 20% compared to the previous generation. Within MiniMax itself, 80% of new code is already generated by M2.5, and it handles 30% of daily tasks.
GLM-5 excels as a "Decision-oriented" Agent: It has the upper hand in scenarios requiring deep reasoning, long-term planning, and complex decision-making. Its MCP Atlas score of 67.8% demonstrates large-scale tool coordination capabilities, while the $4,432 simulated revenue in Vending Bench 2 showcases long-term business planning skills. The 89.7% on τ²-Bench highlights its deep reasoning in specific domains.
Both are neck-and-neck in web search and browsing capabilities—76.3% vs 75.9% on BrowseComp—making them both leaders in this field.
🎯 Agent Scenario Recommendations: Choose M2.5 for high-frequency tool calls and automated coding; choose GLM-5 for complex decision-making and long-term planning. The APIYI (apiyi.com) platform supports both models, allowing you to switch flexibly based on your needs.
MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5: Architecture and Cost Comparison
| Architecture & Cost | MiniMax-M2.5 | GLM-5 |
|---|---|---|
| Total Parameters | 230B | 744B |
| Active Parameters | 10B | 40B |
| Activation Ratio | 4.3% | 5.4% |
| Training Data | — | 28.5 Trillion Tokens |
| Context Window | 205K | 200K |
| Max Output | — | 131K |
| Input Price | $0.15/M (Standard) | $1.00/M |
| Output Price | $1.20/M (Standard) | $3.20/M |
| Output Speed | 50-100 TPS | ~66 TPS |
| Training Chips | — | Huawei Ascend 910 |
| Training Framework | Forge RL | SLIME Asynchronous RL |
| Attention Mechanism | — | DeepSeek Sparse Attention |
| Open Source License | MIT | MIT |
MiniMax-M2.5 Architecture Analysis
The core architectural advantage of M2.5 lies in its "extreme lightweight" design—achieving coding capabilities close to Opus 4.6 with only 10B active parameters. This results in:
- Extremely low inference costs: At $1.20/M for output, it's only 37% of the cost of GLM-5.
- Blazing fast inference speeds: The Lightning version hits 100 TPS, which is 52% faster than GLM-5's ~66 TPS.
- Lower deployment barrier: With only 10B active parameters, deployment on consumer-grade GPUs becomes a real possibility.
GLM-5 Architecture Analysis
GLM-5's 744B total parameters and 40B active parameters give it a much larger knowledge capacity and greater reasoning depth:
- Larger knowledge base: Trained on 28.5 trillion tokens, far exceeding previous generations.
- Deeper reasoning capabilities: 40B active parameters support more complex reasoning chains.
- Domestic computing power independence: Trained entirely on Huawei Ascend chips, achieving full independence in computing resources.
- DeepSeek Sparse Attention: Efficiently handles 200K long-context windows.
Recommendation: For cost-sensitive scenarios with high-frequency calls, M2.5's price advantage is significant (output price is just 37% of GLM-5). We recommend testing the actual cost-performance ratio for your specific tasks on the APIYI platform.
Quick API Integration: MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5
You can use the APIYI platform to call both models through a unified interface, making it easy to compare them side-by-side:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://vip.apiyi.com/v1"
)
# Coding task test - M2.5 excels here
code_task = "Implement a lock-free concurrent queue in Rust"
m25_result = client.chat.completions.create(
model="MiniMax-M2.5",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": code_task}]
)
# Reasoning task test - GLM-5 excels here
reason_task = "Prove that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes (Verification logic for Goldbach's Conjecture)"
glm5_result = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-5",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": reason_task}]
)
Recommendation: Grab some free test credits at apiyi.com and test both models against your specific use cases. Try M2.5 for coding tasks and GLM-5 for complex reasoning to find the solution that fits you best.
FAQ
Q1: What are MiniMax-M2.5 and GLM-5 best at?
MiniMax-M2.5 excels at coding and Agent tool calling—its SWE-Bench score of 80.2% is close to Opus 4.6, and its BFCL score of 76.8% is industry-leading. GLM-5 shines in reasoning and knowledge reliability—boasting 92.7% on AIME, 86.0% on GPQA, and the industry's lowest hallucination rate. Simple rule of thumb: pick M2.5 for coding, and GLM-5 for reasoning.
Q2: What’s the price difference between the two?
MiniMax-M2.5 Standard costs $1.20/M tokens for output, while GLM-5 is $3.20/M tokens, making M2.5 about 2.7 times cheaper. If you go with the M2.5 Lightning high-speed version ($2.40/M), the price is closer to GLM-5 but it's much faster. You can also get recharge discounts by accessing them through the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform.
Q3: How can I quickly compare the actual performance of both models?
We recommend using the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform for unified access:
- Register for an account to get your API Key and free credits.
- Prepare two types of test tasks: coding and reasoning.
- Call both MiniMax-M2.5 and GLM-5 for the same task.
- Compare output quality, response speed, and token consumption.
- Since it uses a unified OpenAI-compatible interface, switching models is as easy as changing the
modelparameter.
Summary
Here are the core takeaways when comparing MiniMax-M2.5 vs. GLM-5:
- Coding: M2.5 is your best bet: SWE-Bench 80.2% vs 77.8% (M2.5 leads by 2.4%), and its BFCL tool-calling score of 76.8% is #1 in the industry.
- Reasoning: GLM-5 takes the lead: With 92.7% on AIME, 86.0% on GPQA, and a score of 50.4 on Humanity's Last Exam, it even outperforms Opus 4.5.
- Knowledge Reliability: GLM-5 wins: It ranks first in the AA-Omniscience hallucination evaluation, making its factual outputs more trustworthy.
- Value: M2.5 offers better bang for your buck: Its output price is only 37% of GLM-5's, and the Lightning version is even faster.
Both models are MIT open-source and use the MoE architecture, but they have very different focus areas: M2.5 is the "King of Coding and Execution Agents," while GLM-5 is the "Pioneer of Reasoning and Knowledge Reliability." We suggest switching between them flexibly on the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform based on your specific needs, and don't forget to check out their recharge events for even better pricing.
📚 References
-
MiniMax M2.5 Official Announcement: M2.5 core coding capabilities and Forge RL training details
- Link:
minimax.io/news/minimax-m25 - Description: Full benchmark data including SWE-Bench 80.2%, BFCL 76.8%, etc.
- Link:
-
GLM-5 Official Release: Zhipu GLM-5's 744B MoE architecture and SLIME training technology
- Link:
docs.z.ai/guides/llm/glm-5 - Description: Includes reasoning benchmark data such as AIME 92.7% and GPQA 86.0%.
- Link:
-
Artificial Analysis Independent Evaluation: Standardized benchmarks and rankings for both models
- Link:
artificialanalysis.ai/models/glm-5 - Description: Independent data covering the Intelligence Index, real-world speed tests, and price comparisons.
- Link:
-
BuildFastWithAI In-depth Analysis: Comprehensive GLM-5 benchmarks and competitor comparisons
- Link:
buildfastwithai.com/blogs/glm-5-released-open-source-model-2026 - Description: Detailed comparison tables featuring Opus 4.5 and GPT-5.2.
- Link:
-
MiniMax HuggingFace: M2.5 open-source model weights
- Link:
huggingface.co/MiniMaxAI - Description: MIT licensed, supporting vLLM/SGLang deployment.
- Link:
Author: APIYI Team
Join the Conversation: Feel free to share your own model comparison results in the comments! For more AI model API integration tutorials, head over to the APIYI apiyi.com tech community.