Author's Note: A deep dive into Claude Code Swarm Mode's inner workings, TeammateTool core architecture, hands-on configuration, and efficiency comparison with traditional single-agent development.
Claude Code Swarm Mode is a major feature released by Anthropic in early 2026 alongside Claude Sonnet 5. This feature transforms Claude Code from a single AI coding assistant into a multi-agent team orchestrator, completely changing the AI-assisted development workflow.
Core Value: By the end of this article, you'll master the full architecture, configuration methods, and best practices of Claude Swarm Mode, achieving a 5-10x boost in development efficiency.
Claude Swarm Mode Core Highlights
| Key Point | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Agent Parallelism | One Leader coordinates multiple specialized Workers in parallel | 5-10x boost in dev efficiency |
| TeammateTool Architecture | 13 core operations supporting agent generation, task allocation, and message sync | Enterprise-grade orchestration |
| Git Worktree Isolation | Each agent has an independent workspace; auto-merges after tests pass | Prevents code conflicts |
| Context Window Distribution | Multiple agents share the context load; single tasks focus on execution | Breaks through context limits |
How Claude Swarm Mode Works
The core idea behind Claude Swarm Mode is simple: instead of having a single Claude instance handle a massive codebase and exhaust its context, it's better to let multiple specialized agents share the workload and execute in parallel.
According to Anthropic's research data, in the BrowseComp evaluation, token usage alone explained 80% of the performance variance. This finding validates the swarm architecture—by distributing work across agents with independent context windows, you can increase the capacity for parallel reasoning.
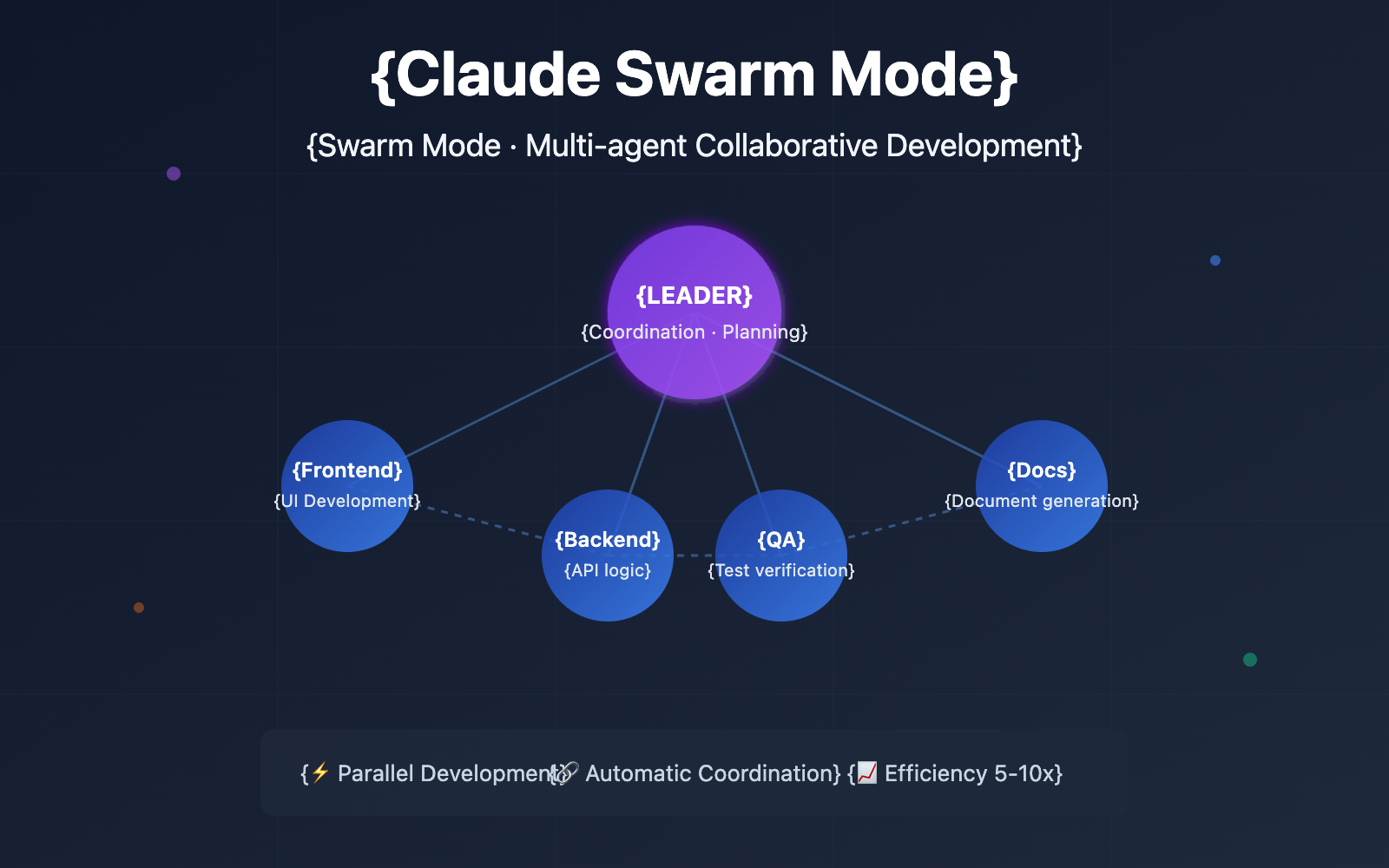
In Swarm Mode, you're no longer talking to a lone AI programmer, but to a Team Lead. This Lead doesn't write code directly; instead, they're responsible for planning, delegating, and coordinating. Once you approve a plan, it generates a team of experts to work in parallel:
- Frontend Agent: Focuses on UI component development.
- Backend Agent: Handles APIs and data logic.
- Testing Agent: Writes and runs test cases.
- Docs Agent: Generates technical documentation.
These agents share a task board and coordinate via a messaging system, achieving true parallel development.
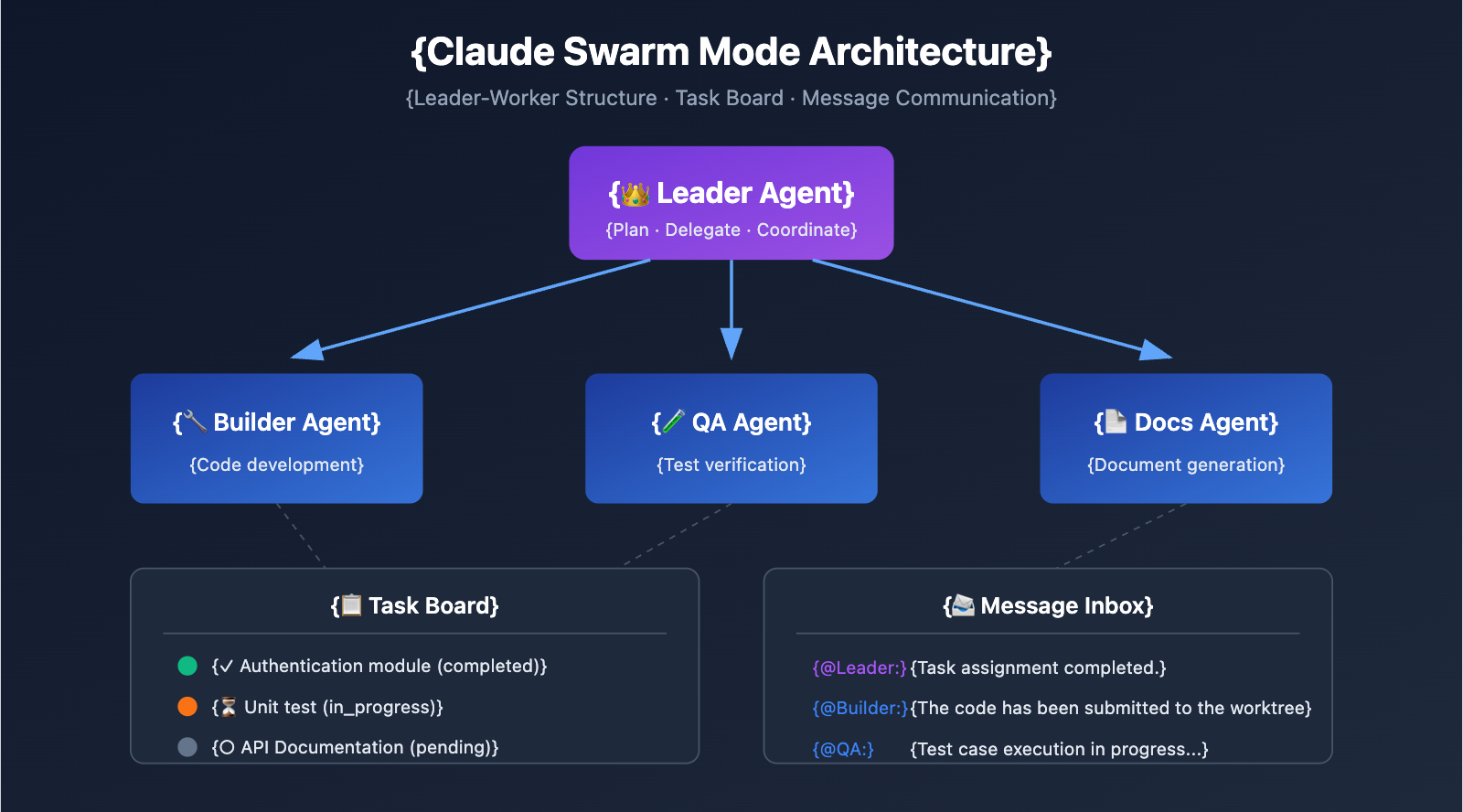
Claude Swarm Mode: TeammateTool Architecture Deep Dive
TeammateTool is the core orchestration layer of Claude Code's Swarm mode, providing 13 distinct operations for managing agents.
TeammateTool: 13 Core Operations at a Glance
| Operation Type | Operation Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Team Management | spawnTeam | Create a new team of agents |
| Team Management | discoverTeams | Discover available teams |
| Team Management | requestJoin | Request to join an existing team |
| Task Allocation | assignTask | Assign a task to a specific agent |
| Task Allocation | claimTask | An agent claims a task |
| Task Allocation | completeTask | Mark a task as completed |
| Communication | broadcastMessage | Broadcast a message to all members |
| Communication | sendMessage | Send a private message to a specific agent |
| Communication | readInbox | Read the message inbox |
| Decision-Making | voteOnDecision | Vote on a specific decision |
| Decision-Making | proposeChange | Propose a code change |
| Lifecycle | shutdown | Gracefully shut down an agent |
| Lifecycle | cleanup | Clean up team resources |
Swarm Mode File System Structure
Claude's Swarm mode uses a file-system-based coordination mechanism:
~/.claude/
├── teams/
│ └── {team-name}/
│ ├── config.json # Team metadata, member list
│ └── messages/ # Inter-agent message inbox
└── tasks/
└── {team-name}/ # Team task list
The advantages of this architecture include:
- High Observability: Since all states are stored as files, it's incredibly easy to debug and monitor what's happening.
- Persistence: Agents can recover their state even after a restart.
- Low Coupling: Agents collaborate through a loosely coupled file system rather than complex direct dependencies.
🎯 Tech Tip: If you want to dive deeper into the underlying implementation of TeammateTool, you can use the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform to access the Claude API for experimental development and testing.
5 Steps to Get Started with Claude Swarm Mode
Step 1: Update to the Latest Claude Code
Make sure your Claude Code is on the latest version, as the Swarm feature has been officially released:
npm update -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
Step 2: Configure the Swarm Protocol
Define your Swarm protocol in your project's CLAUDE.md or within your system prompt:
# Swarm Protocol
Triggers
- "Activate Swarm Mode"
- "Activate Swarm Mode"
Roles
- Manager: Scrum Master, responsible for planning and coordination, doesn't write code directly
- Builder: Focuses on code development
- QA: Focuses on testing and quality assurance
- Docs: Focuses on documentation writing
Rules
- Use TeammateTool for agent generation and task allocation
- Each agent works in an independent Git Worktree
- Code can only be merged after passing tests
### Step 3: Launch the Swarm and Create Tasks
```javascript
// === Create Team ===
Teammate({ operation: "spawnTeam", team_name: "feature-dev" })
// === Create Task List ===
TaskCreate({
subject: "实现用户认证模块",
description: "包含登录、注册、JWT Token 管理",
activeForm: "开发用户认证..."
})
TaskCreate({
subject: "编写认证模块单元测试",
description: "覆盖所有认证场景",
activeForm: "编写单元测试..."
})
Step 4: Generate Specialized Agents
// === Generate Builder Agent ===
Task({
team_name: "feature-dev",
name: "auth-builder",
subagent_type: "general-purpose",
prompt: "你是认证模块开发专家,负责实现安全的用户认证系统",
run_in_background: true
})
// === Generate QA Agent ===
Task({
team_name: "feature-dev",
name: "auth-qa",
subagent_type: "general-purpose",
prompt: "你是 QA 工程师,负责编写和执行认证模块的测试用例",
run_in_background: true
})
Step 5: Monitoring and Cleanup
// === Monitor Task Progress ===
TaskList({ team_name: "feature-dev" })
// === Cleanup after Task Completion ===
Teammate({ operation: "cleanup", team_name: "feature-dev" })
Tip: Get your Claude API Key via APIYI (apiyi.com). The platform supports the full range of Claude models, making it easy to switch between them for different scenarios.
Claude Swarm Mode vs. Single Agent Mode

| Comparison Dimension | Single Agent Mode | Swarm Mode | Advantage Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development Efficiency | 1x (Baseline) | 5-10x | Multi-agent parallelism, linear scaling |
| Context Capacity | 200K per window | Cumulative across windows | Each agent has an independent context |
| Code Conflicts | None (Single-threaded) | Automatic isolation | Git Worktree isolation |
| Task Complexity | Best for simple tasks | Best for large projects | Divide and conquer strategy |
| Token Consumption | 1x (Baseline) | 4-15x | Trading cost for efficiency |
| Debugging Difficulty | Simple | Medium | Requires understanding orchestration logic |
Swarm Mode Use Case Analysis
Recommended for Swarm Mode:
- Large feature development (involving 5+ file changes)
- Code refactoring projects
- Full-stack development tasks (Frontend + Backend + Testing)
- Code review pipelines
Recommended for Single Agent:
- Simple bug fixes
- Single file modifications
- Rapid prototype validation
- Scenarios with limited token budgets
Pro Tip: According to a Gartner report, consultations for multi-agent systems grew by 1445% from Q1 2024 to Q2 2025. By the end of 2026, it's expected that 40% of enterprise applications will include task-specific AI agents. We recommend experiencing and evaluating this technology trend early via the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform.
Claude Swarm Mode Git Worktree Isolation Mechanism
One of the smartest things about Swarm Mode is how it handles file conflicts. Each agent works in an independent Git Worktree, preventing them from overwriting each other's code changes.
Workflow
- Leader Creates a Plan → Breaks down tasks and assigns them to Workers.
- Worker Creates a Worktree → Each agent gets an independent copy of the code.
- Parallel Development → Multiple agents write code simultaneously.
- Automated Testing → Each agent runs tests upon completion.
- Merge to Main Branch → Code is merged only if tests pass.
This mechanism ensures that even if five agents are coding at once, the main branch stays stable.
Token Cost Considerations
The swarm architecture definitely consumes more tokens:
- Single-agent conversation: 1x Tokens
- Multi-agent system: Approx. 4-15x Tokens
For economic feasibility, the task's value needs to be high enough to justify the increased performance cost. Therefore, we recommend using Swarm Mode for high-value, complex tasks.
🎯 Cost Tip: Use the Claude API through the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform. They offer flexible billing, making it easier to manage token costs in multi-agent scenarios.
FAQ
Q1: How does Claude Swarm Mode avoid code conflicts between agents?
Swarm Mode uses the Git Worktree mechanism, where each agent operates in an independent working directory. They modify copies of the code, and changes are only merged into the main branch after passing tests. This architecture fundamentally eliminates conflict issues during parallel development.
Q2: Will token consumption be very high in Swarm Mode?
Yes, multi-agent systems typically consume 4 to 15 times more tokens. We recommend using Swarm Mode for high-value tasks (like large feature development or full-stack projects), while sticking to single-agent mode for simpler tasks. You can monitor and control token consumption through the APIYI (apiyi.com) platform.
Q3: How can I quickly try out Claude Swarm Mode?
Recommended steps:
- Update Claude Code to the latest version.
- Configure the Swarm protocol in your project (
CLAUDE.md). - Get a Claude API Key via APIYI (apiyi.com).
- Use the "Activate Swarm Mode" command to start.
- Assign tasks and watch the multi-agent collaboration in action.
Summary
Key takeaways of Claude Swarm mode:
- Architectural Innovation: Moving from single agents to Leader-Worker multi-agent teams, enabling true parallel development.
- TeammateTool: 13 core operations supporting enterprise-grade agent orchestration.
- Git Worktree Isolation: Automatically handles code conflicts during parallel development.
- Efficiency Boost: Can achieve 5-10x development efficiency gains on large-scale projects.
- Cost Trade-offs: Increased token consumption makes it best suited for high-value, complex tasks.
As Anthropic transitions Swarm mode from a hidden feature to an official release, multi-agent collaborative development is becoming the new standard for AI programming.
We recommend using APIYI (apiyi.com) to access the Claude API. The platform supports the full range of Claude models, making it easy to practice multi-agent development in Swarm mode.
References
-
What Is the Claude Code Swarm Feature?: Official analysis of Claude Code's Swarm functionality.
- Link:
atcyrus.com/stories/what-is-claude-code-swarm-feature - Description: Detailed introduction to how Swarm mode works and how to use it.
- Link:
-
Claude Code Swarm Orchestration Skill: A complete guide to using TeammateTool.
- Link:
gist.github.com/kieranklaassen/4f2aba89594a4aea4ad64d753984b2ea - Description: Includes detailed example code for all 13 operations.
- Link:
-
Claude Code's Hidden Multi-Agent System: In-depth technical analysis of Swarm mode.
- Link:
paddo.dev/blog/claude-code-hidden-swarm/ - Description: Analyzes the internal implementation mechanisms of Swarm mode.
- Link:
-
Claude-Flow Agent Orchestration Platform: A third-party multi-agent orchestration framework.
- Link:
github.com/ruvnet/claude-flow - Description: An open-source Claude multi-agent orchestration tool, useful as a learning reference.
- Link:
-
Hacker News: Claude Code's new hidden feature: Swarms: Community discussion.
- Link:
news.ycombinator.com/item?id=46743908 - Description: Discussions and practical experiences shared by the developer community regarding Swarm mode.
- Link:
Author: APIYI Team
Technical Exchange: Feel free to join the discussion in the comments. For more resources, visit the APIYI (apiyi.com) technical community.