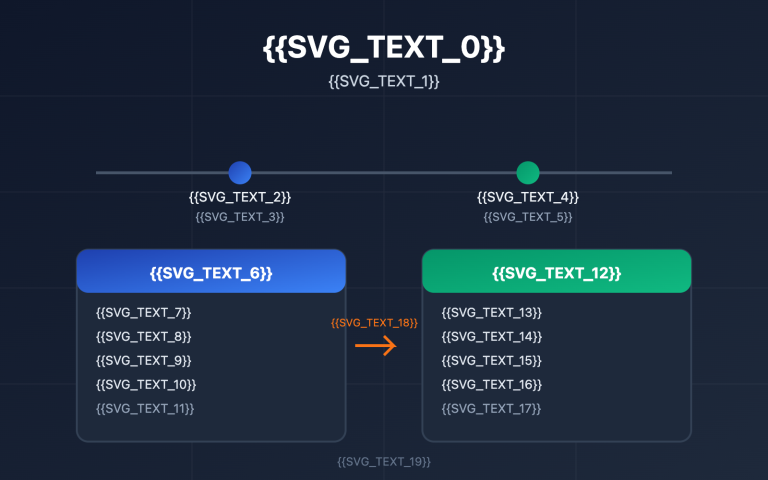
Author's Note: This article provides a deep dive into the core differences between OpenClaw AI Agent and traditional RPA. We'll analyze them across five dimensions—including decision-making, adaptability, and technical architecture—to help you choose the automation solution that fits your needs best.
"RPA can simulate mouse clicks, and OpenClaw can control the desktop too—so what's the difference?" This is likely to be the most common question in the automation field by 2026. On the surface, both can handle desktop-level tasks, but their underlying logic is worlds apart. In this post, we'll break down the 5 core dimensions where OpenClaw AI Agent and traditional RPA diverge, helping you understand the true nature of this automation revolution.
Core Value: By the end of this article, you'll clearly understand the fundamental differences between AI Agents and RPA. You'll know exactly which one to pick for different scenarios and how to combine their strengths to build a hybrid automation architecture.
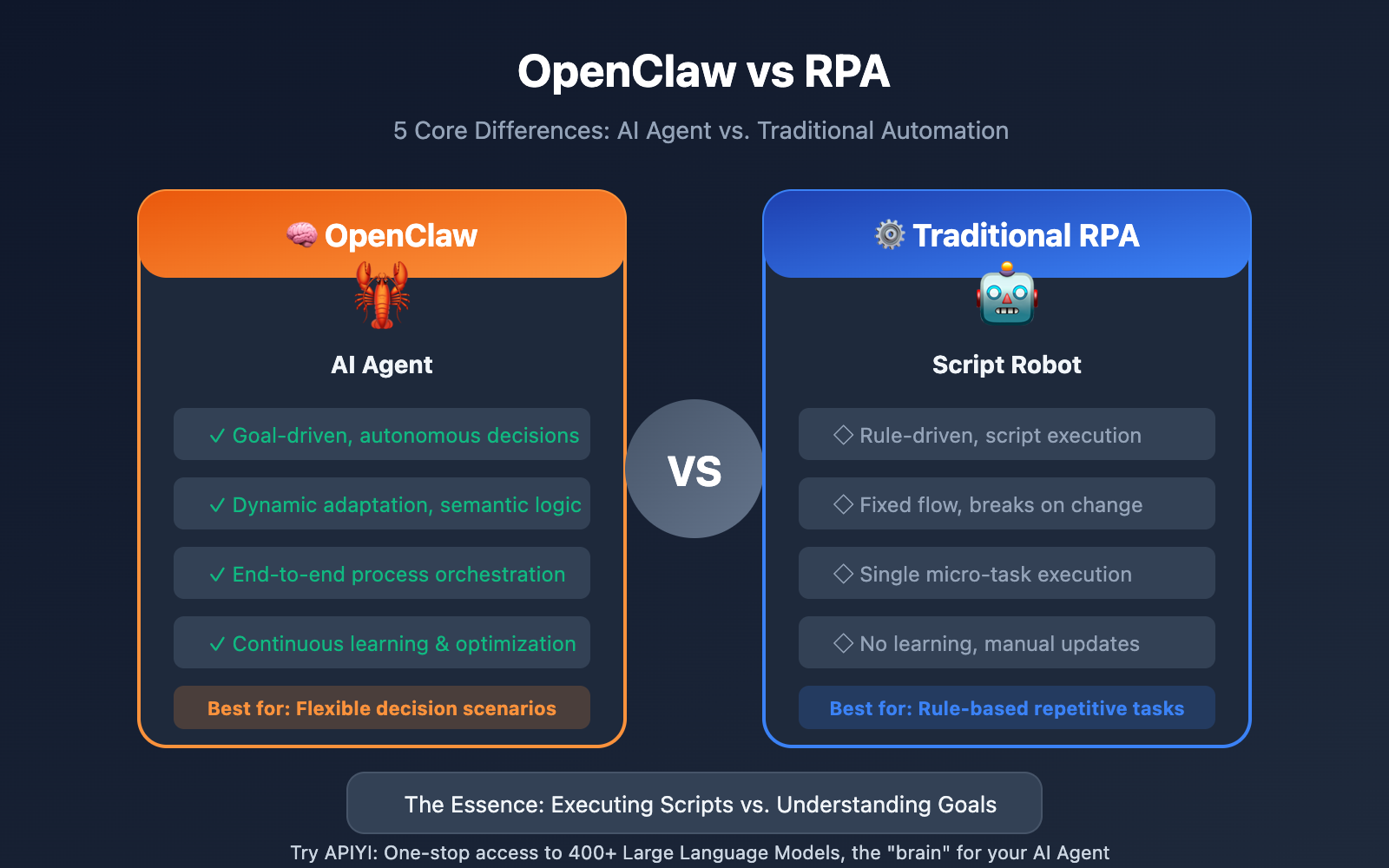
Quick Look: OpenClaw vs. RPA Core Differences
| Dimension | OpenClaw (AI Agent) | Traditional RPA |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | Goal-driven, autonomous | Rule-driven, script-based |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptive, dynamic adjustments | Fixed flow, breaks on change |
| Input Type | Unstructured (Natural Language) | Structured (Fixed Formats) |
| Work Scope | End-to-end process orchestration | Single micro-task execution |
| Learning Ability | Continuous learning, self-optimizing | No learning, manual updates required |
A Simple Example
Let's say the task is "Handle customer complaint emails":
The Traditional RPA Approach:
- Open inbox → Filter emails based on specific rules → Copy content to the ticket system → Send a template reply.
- If the email format changes or the subject line doesn't match the rule, the whole process breaks.
- A developer has to manually update the script to get it running again.
The OpenClaw Approach:
- Understands the high-level goal: "Handle customer complaints."
- Autonomously determines which emails are actual complaints and how urgent they are.
- Crafts a personalized reply based on the specific content, or escalates to a human if necessary.
- Email format changed? No problem. The AI understands the context regardless of the layout.
That's the fundamental difference between "executing a script" and "understanding a goal."
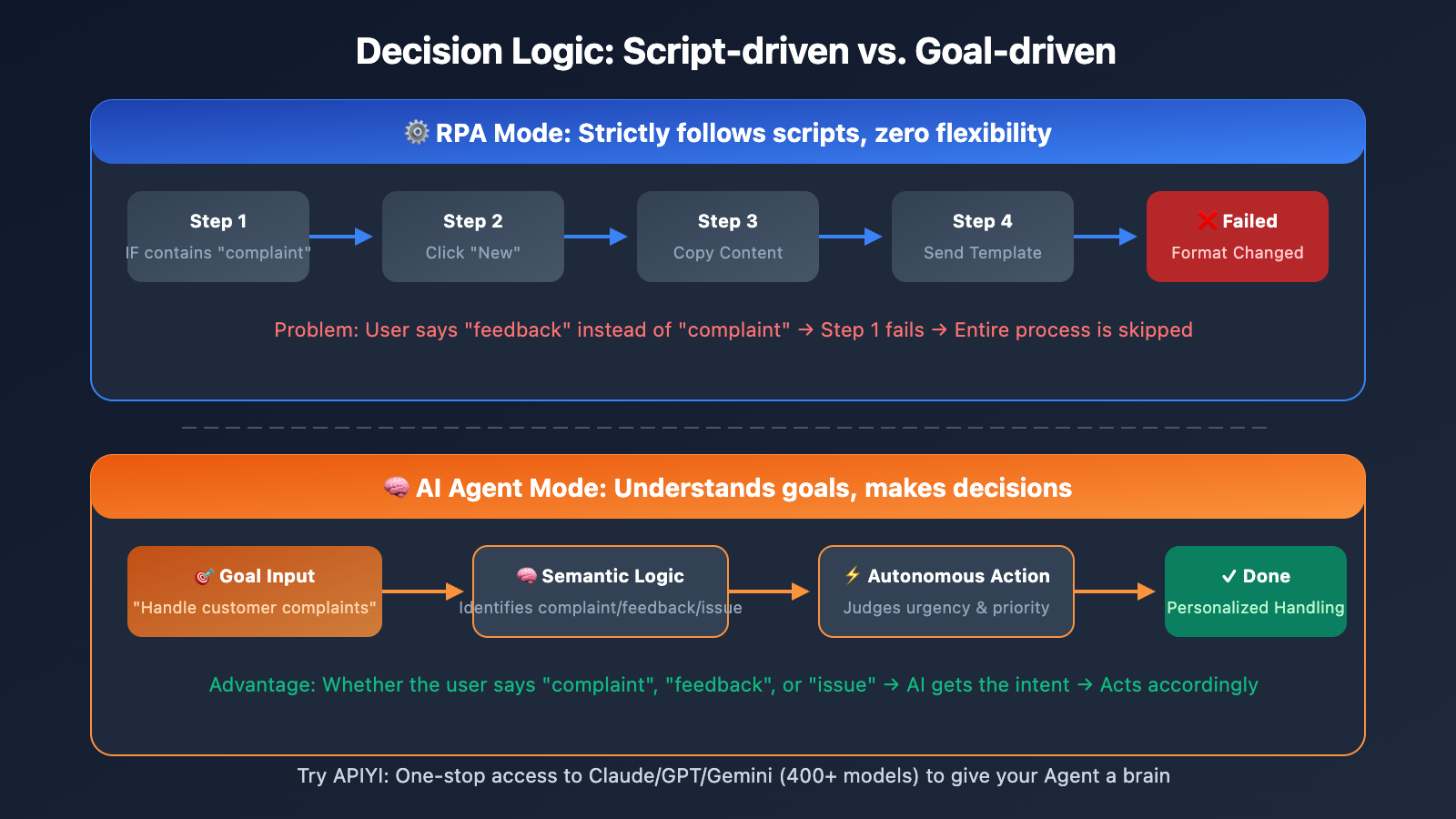
OpenClaw vs. RPA: 5 Core Differences Explained
Difference 1: Decision Making — Script vs. Reasoning
Traditional RPA: Rule-Driven
RPA systems execute a strict set of predefined instructions. You tell it exactly what to do, and it follows the script to the letter. There's zero flexibility—if a rule isn't explicitly written, the task won't be executed.
# RPA Script Example (Pseudo-code)
IF email.subject CONTAINS "Complaint" THEN
CLICK button("New Ticket")
COPY email.body TO field("Description")
CLICK button("Submit")
ELSE
SKIP
END IF
The problem? If a user expresses a complaint using words like "feedback," "unsatisfied," or "issue," the RPA will completely fail to recognize it.
OpenClaw: Goal-Driven
OpenClaw's AI Agents take a completely different approach—you define the goal, not the steps, and the Agent decides how to achieve it.
# OpenClaw Instruction
"Help me process all customer complaint emails. Prioritize urgent ones,
create tickets for standard ones, and archive those that are resolved."
The Agent will:
- Understand what a "complaint" is (even if the user doesn't use that specific word).
- Judge the level of urgency (based on sentiment, timing, and customer tier).
- Autonomously choose the best processing method.
- Ask the user for clarification instead of crashing when it encounters uncertainty.
🎯 Technical Insight: OpenClaw's decision-making power comes from the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Through APIYI, you can access over 400 models like Claude, GPT, and Gemini in one place, providing your Agent with a world-class "brain."
Difference 2: Adaptability — Fragile vs. Resilient
Traditional RPA: Change Equals Crash
The biggest pain point of RPA is its fragility. If the target system changes even slightly, the script is likely to break:
| Type of Change | RPA Consequence |
|---|---|
| Button moved | Click fails, process stops |
| Field name modified | Data entered in the wrong place |
| Page loads slowly | Timeout error |
| New verification step | Completely stuck |
| UI redesign | Script needs a total rewrite |
According to industry stats, 30-40% of maintenance costs in enterprise RPA projects are spent just fixing these "broken script" issues.
OpenClaw: Dynamic Adaptation
OpenClaw's AI Agents operate the interface through "understanding" rather than "memorization":
# How OpenClaw references elements
openclaw browser snapshot
# Output: [ref=1] Login Button [ref=2] Username Input [ref=3] Password Input
openclaw browser click --ref 1
# The Agent understands the semantics of "Login Button" rather than remembering coordinates
Even if a button moves or its name changes, as long as the semantics remain similar, the Agent can still identify it correctly. This semantic-based operation gives OpenClaw a level of resilience that traditional RPA simply can't match.
Difference 3: Input Processing — Structured vs. Unstructured
| Input Type | RPA Capability | OpenClaw Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Excel Spreadsheets | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Excellent |
| Fixed-format PDFs | ✅ Via OCR | ✅ Native Understanding |
| Free-form Emails | ❌ Cannot process | ✅ Understands Intent |
| Voice Commands | ❌ Not supported | ✅ Supported |
| Chat Messages | ❌ Needs templates | ✅ Natural Dialogue |
| Handwritten Docs | ❌ High error rate | ✅ Visual Understanding |
Real-world Case:
When traditional RPA processes invoices, it requires the formats to be highly consistent. If Vendor A and Vendor B use different layouts, you have to write separate extraction rules for each.
OpenClaw, however, can "read" any invoice format—it understands semantic concepts like "Total Amount," "Vendor Name," and "Date," rather than relying on fixed coordinate positions.
Difference 4: Scope of Work — Micro-tasks vs. End-to-End
Traditional RPA: Focused on Micro-tasks
RPA excels at automating discrete, small steps:
- Copying and pasting data
- Filling out forms
- Sending template emails
- Clicking buttons
But it can't "see" the bigger workflow or manage the relationships between tasks.
OpenClaw: Orchestrating Full Processes
OpenClaw's Agentic AI is capable of full process orchestration:
User: Help me finish this month's expense reimbursement.
OpenClaw completes autonomously:
1. Collects all relevant invoices and receipts (emails, photos).
2. Identifies the type, amount, and date of each document.
3. Categorizes them per company policy (travel, meals, office supplies).
4. Fills out the reimbursement system forms.
5. Uploads attachments and submits.
6. Notifies finance for review.
7. Tracks approval status and provides feedback.
This end-to-end orchestration is something traditional RPA just can't do. RPA would likely require seven independent scripts and would still struggle with exceptions and decision points within the flow.
Difference 5: Learning Ability — Static vs. Evolving
Traditional RPA: Zero Learning Capability
An RPA bot performs the exact same operation every time. If a process needs optimization, a developer must manually modify the script. It doesn't learn from its mistakes, and it doesn't get better over time.
OpenClaw: Continuous Evolution
OpenClaw features multi-layered learning capabilities:
| Learning Type | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Session Memory | Remembers user preferences and historical context |
| Skill Acquisition | Learns new "Skills" to expand its capabilities |
| Feedback Optimization | Adjusts behavior based on user feedback |
| Pattern Recognition | Identifies repetitive tasks and suggests automation |
One user shared: "I asked OpenClaw to check my token usage and suggest optimizations. After analyzing it, it proposed a series of adjustments that cut my token consumption in half once implemented."
OpenClaw vs. RPA Technical Architecture Comparison
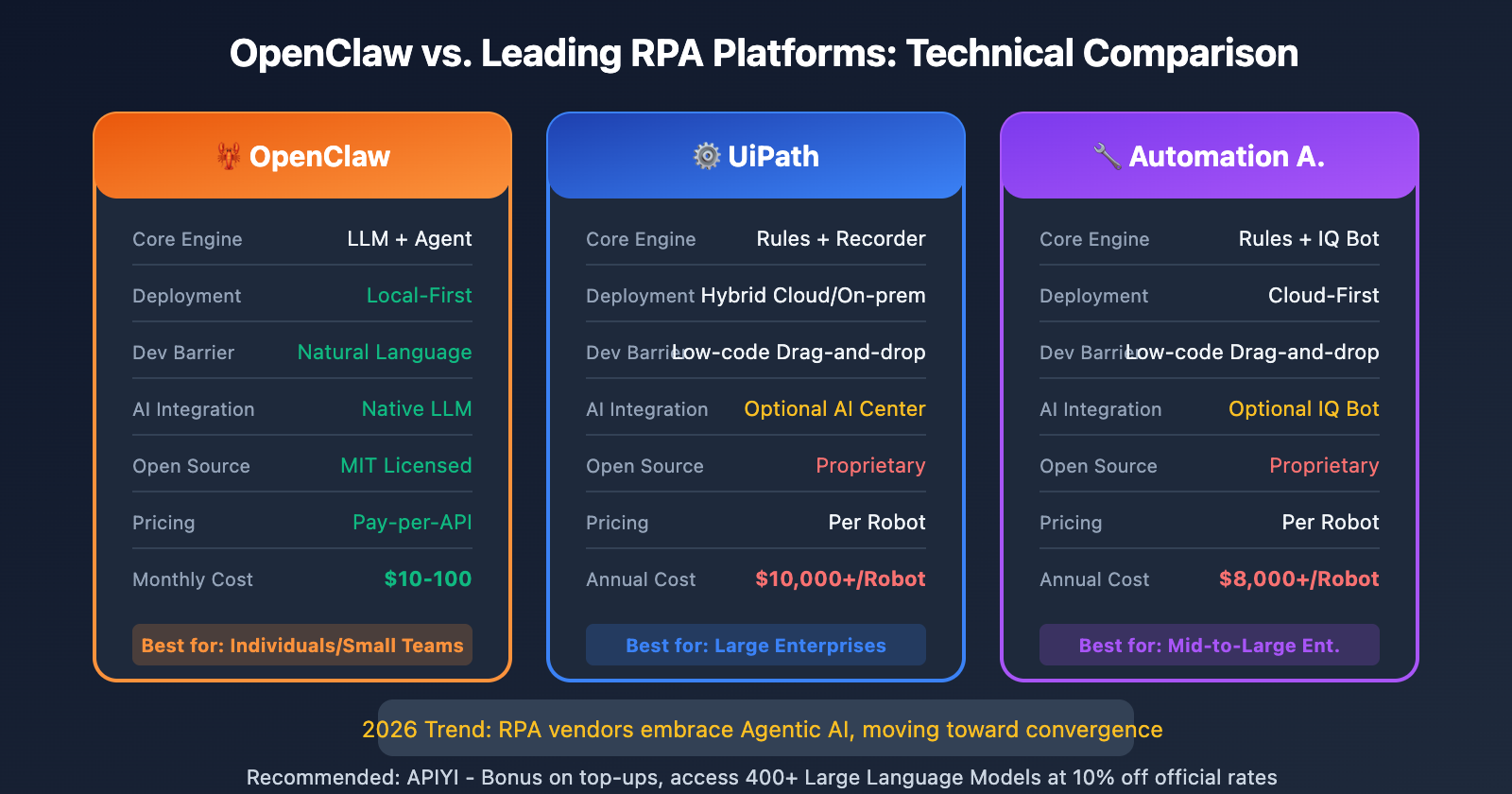
| Technical Dimension | OpenClaw | UiPath | Automation Anywhere |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Engine | LLM + Agent Framework | Rule Engine + Recorder | Rule Engine + IQ Bot |
| Deployment | Local-First | Hybrid Cloud/On-prem | Cloud-First |
| Dev Barrier | Natural Language | Low-code Drag-and-drop | Low-code Drag-and-drop |
| AI Integration | Native LLM Driven | Optional AI Center | Optional IQ Bot |
| Open Source | MIT Licensed | Proprietary | Proprietary |
| Pricing Model | Pay-per-API | Per Robot | Per Robot |
Industry Trend: Fusion, Not Replacement
It's worth noting that by 2026, RPA giants are also actively embracing Agentic AI:
- UiPath launched its Agentic Automation platform, claiming an "evolution from RPA to Agentic AI."
- Automation Anywhere's AARI system has enhanced human-machine collaboration and decision-making.
- Microsoft Power Automate is deeply integrating Copilot AI capabilities.
Gartner predicts that Agentic automation will achieve 25-60% higher coverage than traditional RPA, with significantly lower error rates.
Trend Insight: The future isn't about AI Agents completely replacing RPA; it's about the two merging. RPA acts as the "muscles" for deterministic tasks, while AI Agents serve as the "brain" for handling decisions and exceptions. By using APIYI to access various AI models, you can add an intelligent decision layer to your existing RPA workflows.
Selection Guide: OpenClaw vs. RPA Use Cases
When to Choose Traditional RPA
| Scenario Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|
| Highly rule-based, zero variability | Bank reconciliation, tax filings |
| Audit trails required | Compliance operations, financial records |
| Millions of repetitive executions | Large-scale data migration |
| Existing enterprise RPA investment | Extending existing UiPath workflows |
When to Choose OpenClaw
| Scenario Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|
| Natural language understanding required | Customer service email processing, meeting minutes |
| Frequently changing processes | Web automation, data scraping |
| Autonomous decision-making required | Intelligent scheduling, exception handling |
| Personal productivity tools | Schedule management, info aggregation |
| Cross-platform messaging | WhatsApp + Email + Slack |
Hybrid Architecture: Best Practices
The most successful automation strategies often combine both:
Invoice Processing Hybrid Architecture Example:
1. RPA handles: Downloading invoice PDFs from a fixed location (Deterministic task)
↓
2. OpenClaw handles: Understanding invoice content, extracting key fields (Semantic understanding)
↓
3. RPA handles: Writing data into the ERP system (Deterministic task)
↓
4. OpenClaw handles: Determining if manual review is needed (Decision-making)
This architecture combines RPA's stability with the intelligence of an AI Agent, achieving a "1+1>2" effect.
OpenClaw Desktop Automation Capabilities Explained
Many people are curious about what "desktop-level" tasks OpenClaw can actually handle. Here's a breakdown of its core capabilities:
| Capability Category | Specific Functions | Technical Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Shell Control | Execute system commands, scripts | Direct system shell calls |
| File Management | Read/write, move, search files | Local file system APIs |
| Browser Control | Navigation, clicks, form filling, screenshots | CDP (Chrome DevTools Protocol) |
| Messaging Platforms | WhatsApp/Telegram/Slack, etc. | Platform SDK integrations |
| Scheduled Tasks | Heartbeat active wake-up | Cron + Webhook |
| Voice Interaction | macOS menu bar voice control | Local TTS + STT |
Security Tip: OpenClaw's powerful capabilities come with high risks. The official recommendation is not to run it on your primary computer containing sensitive data; instead, prioritize using Docker sandbox isolation.
FAQ
Q1: Can OpenClaw completely replace RPA?
Not completely, at least not yet. For highly regulated enterprise scenarios that require strict audit trails (like core banking operations), the predictability and auditability of traditional RPA are still irreplaceable. OpenClaw is better suited for personal productivity and scenarios requiring flexible decision-making. The future trend is more about fusion than replacement.
Q2: How does the cost of OpenClaw compare to RPA?
The cost structures are totally different:
- RPA: Charged per bot; UiPath Enterprise is roughly $10,000+/year/bot.
- OpenClaw: The software is free and open-source; you pay based on AI API consumption. Light users might spend $10-30/month.
For individual users and small teams, OpenClaw is much more affordable. You can lower your API costs even further by taking advantage of top-up bonuses on APIYI (apiyi.com).
Q3: Can enterprises use OpenClaw?
You'll need to evaluate this carefully. Right now, OpenClaw is a better fit for tech-savvy users and personal use cases. Enterprises need to consider:
- Security risks (Shell access, credential storage)
- Compliance requirements (audit trails, data isolation)
- Maintenance costs (requires a technical team for upkeep)
For enterprise-grade AI automation needs, you might want to look into commercial solutions like UiPath Agentic Automation or Microsoft Power Automate + Copilot.
Summary
Here are the 5 key differences between OpenClaw and RPA:
- Decision-making: RPA executes scripts; OpenClaw understands goals.
- Adaptability: RPA is fragile and breaks easily; OpenClaw adapts dynamically.
- Input Handling: RPA requires structured data; OpenClaw understands natural language.
- Scope of Work: RPA focuses on micro-tasks; OpenClaw orchestrates end-to-end processes.
- Learning Ability: RPA is static; OpenClaw evolves continuously.
Which one should you choose?
- Highly regulated with a need for audit trails → Traditional RPA
- Need for flexible decision-making and natural language interaction → OpenClaw
- Best practice → A hybrid architecture that plays to the strengths of both.
No matter which solution you pick, AI capability is the core driver. We recommend using APIYI (apiyi.com) to access over 400+ Large Language Models to give your automation workflows a powerful "brain." The platform offers top-up bonuses, making your costs even lower than 90% of official pricing.
📚 References
⚠️ Link Format Note: All external links use the
Resource Name: domain.comformat. This makes them easy to copy while remaining non-clickable to prevent SEO weight loss.
-
TechTarget: AI Agent vs RPA Comparison: Authoritative technical analysis
- Link:
techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/tip/Compare-AI-agents-vs-RPA-Key-differences-and-overlap - Description: A detailed comparison of the technical differences between AI Agents and RPA.
- Link:
-
UiPath Agentic Automation: The RPA giant's AI transformation
- Link:
uipath.com/platform/agentic-automation - Description: UiPath's official introduction to their Agentic AI strategy.
- Link:
-
OpenClaw Official Documentation: Browser control capabilities
- Link:
docs.openclaw.ai/tools/browser - Description: Technical details regarding OpenClaw's desktop automation technology.
- Link:
-
Zapier: Agentic AI vs RPA: A beginner-friendly comparison guide
- Link:
zapier.com/blog/agentic-ai-vs-rpa - Description: A comparison article that's perfect for those just getting started.
- Link:
-
Gartner RPA Magic Quadrant 2025: Authoritative industry assessment
- Link:
gartner.com/reviews/market/robotic-process-automation - Description: Analysis of the RPA market landscape and current trends.
- Link:
Author: Technical Team
Tech Talk: Feel free to join the discussion in the comments. For more automation solutions, you can visit the APIYI apiyi.com technical community.