5 Implementation Solutions for LLM API Web Query Capabilities
In AI application development, web query capability for large model APIs has become one of the core functional requirements. Whether for real-time information retrieval, news analysis, or dynamic data queries, web capabilities can significantly enhance the practicality and accuracy of AI applications. However, many developers face a key challenge when integrating large model APIs: how to enable models with web query capabilities? This article will provide an in-depth comparison of 5 mainstream technical solutions, from native tool calling, encapsulated web capabilities, reverse APIs, MCP protocol, to workflow orchestration, analyzing each solution’s technical principles, stability, costs, and applicable scenarios to help you choose the optimal solution.
Why LLM APIs Need Web Capabilities
Limitations of Knowledge Cutoff Dates
All large language models have fixed knowledge cutoff dates. For example:
- GPT-4 Turbo: December 2023
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet: August 2024
- Gemini 3 Series: January 2025
This means models cannot answer real-time questions beyond their cutoff dates, such as:
- “What’s today’s stock market performance?”
- “What features were released in the latest iPhone?”
- “What were yesterday’s NBA game results?”
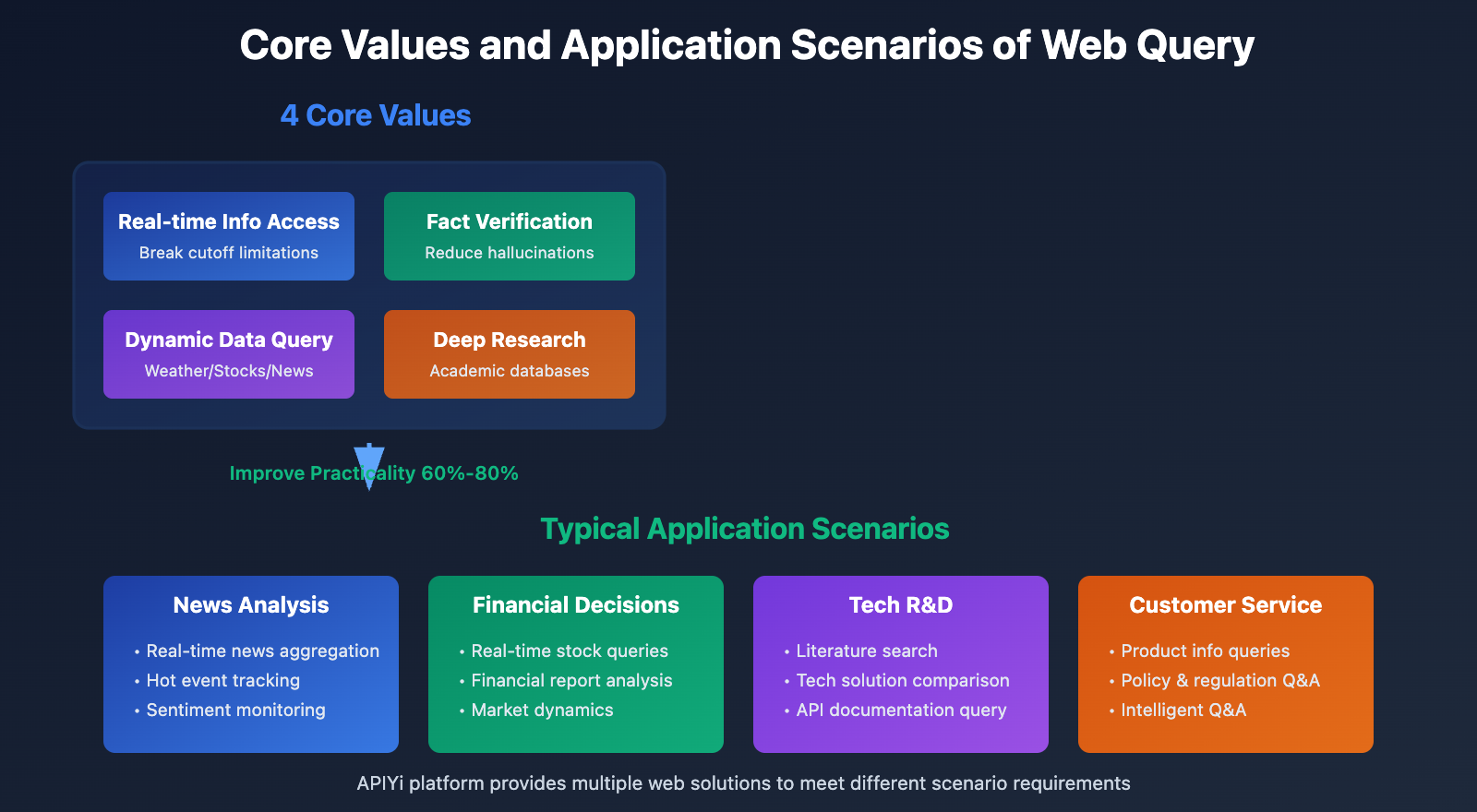
Core Value of Web Query
1. Real-time Information Access: Break through knowledge cutoff limitations to obtain latest data
2. Fact Verification: Verify model output accuracy and reduce hallucination risks
3. Dynamic Data Queries: Weather, stock prices, news, and other real-time changing information
4. Deep Research: Combine search engines and academic databases for in-depth analysis
🎯 Application Scenarios: In news analysis, financial decision-making, technology R&D, customer service, and other scenarios, web query capabilities can improve AI application practicality by 60%-80%. It’s recommended to access models with web query support through the APIYi (apiyi.com) platform, which integrates multiple web solutions to help developers quickly implement web functionality.
Solution 1: Native Tool Calling (Function Calling)
Technical Principles
Some production-ready large language models have built-in Tool Calling (Function Calling) or Tools API functionality, allowing developers to define internet search tools that models can proactively invoke when needed.
Workflow:
- Developers define internet search tools (e.g.,
web_search) - Users ask questions requiring internet access
- Model identifies the requirement and outputs a tool call request
- Developer backend executes actual search (calling Google, Bing API, etc.)
- Search results are returned to the model
- Model generates final answer based on search results
Supported Models
| Model | Tool Calling Support | Official Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 Turbo | ✅ Function Calling | OpenAI Docs |
| GPT-4o | ✅ Function Calling | OpenAI Docs |
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | ✅ Tool Use | Anthropic Docs |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | ✅ Function Calling | Google AI Docs |
| Gemini 3 Series | ✅ Function Calling | Google AI Docs |
Technical Implementation Example
import openai
# Define internet search tool
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"description": "Search the internet for real-time information",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Search keywords"
}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
}
}
]
# Call the model
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Beijing today?"}],
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
# If model requests tool invocation
if response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
tool_call = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
# Execute actual search (call Google Search API, etc.)
search_result = execute_web_search(tool_call.function.arguments)
# Return results to the model
final_response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Beijing today?"},
response.choices[0].message,
{"role": "tool", "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, "content": search_result}
]
)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- ✅ Official support with high stability
- ✅ Flexible and controllable, customizable search logic
- ✅ Suitable for complex workflows, can combine multiple tools
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Requires implementing search logic and API integration yourself
- ❌ Higher development costs, need to handle multi-turn dialogues for tool calls
- ❌ Requires paid search APIs (Google, Bing, etc.)
Use Cases: Enterprise-level applications requiring highly customized internet search logic, willing to invest in development costs.
💡 Development Advice: For scenarios requiring fine-grained control over search logic, the tool calling solution is recommended. Call models with tool support through the API易 apiyi.com platform, which provides detailed tool calling examples and debugging tools to simplify the development process.
Solution 2: Encapsulated Internet Capability (Built-in Internet Access)
Technical Principles
Some models or service providers have built-in encapsulated internet search capabilities. Developers don’t need to manually define tools; the model automatically determines whether internet access is needed and executes searches.
Workflow:
- User asks a question
- Model automatically identifies if internet access is needed
- Model internally calls search services (transparent processing)
- Directly returns answers containing real-time information
Supported Services
| Service | Internet Method | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Perplexity AI | Built-in Internet | Focuses on real-time search with source citations |
| Google Gemini (Web Version) | Built-in Internet | Automatic internet access, no configuration needed |
| Claude (Web Version) | Built-in Internet | Partial support in 2025 |
| You.com | Built-in Internet | Search engine + AI dialogue |
Technical Implementation Example
# Perplexity API Example
import requests
response = requests.post(
"https://api.perplexity.ai/chat/completions",
headers={
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
json={
"model": "llama-3.1-sonar-large-128k-online",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Beijing today?"}
]
}
)
# Model automatically searches online and returns answers with real-time information
print(response.json()["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- ✅ Ready to use out of the box, no additional development needed
- ✅ Extremely low development costs, completed in a single call
- ✅ Automatic source citation, increases credibility
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Black box processing, cannot control search logic
- ❌ May incur additional costs (some services charge per internet access)
- ❌ Limited model selection, mainly specific service providers
Use Cases: Rapid prototyping, simple internet search requirements, no need for fine-grained control over search processes.
🚀 Quick Start: For startup teams and MVP validation, the encapsulated internet solution is recommended. The API易 apiyi.com platform has integrated models with built-in internet access like Perplexity, ready to use out of the box, with integration completed in 5 minutes.
Solution 3: Reverse Engineered API (Unofficial, Low Stability)
Technical Principles
Reverse engineered APIs work by simulating web interface requests, calling the official web version’s internet connectivity features. For example, claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-all is implemented by reverse engineering the claude.ai web interface.
Workflow:
- Reverse engineers analyze web version requests
- Simulate browser requests, masquerading as real users
- Call the web version’s internet search functionality
- Parse returned data and encapsulate it in API format
Typical Cases
Claude Reverse Engineered API:
claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-all: Simulates claude.ai web version, supports internet queries- Provided by third-party service providers, integrated in platforms like APIyi
ChatGPT Reverse Engineered API:
gpt-4-web: Simulates chat.openai.com, supports internet and plugins- Provided by some service providers
Technical Implementation Example
# Call reverse engineered Claude API through APIyi platform
import openai
client = openai.OpenAI(
api_key="YOUR_APIYI_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1"
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-all", # Reverse engineered model, supports internet
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Silicon Valley Bank's stock price today?"}
]
)
# Model will automatically search the internet and return real-time answers
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- ✅ Access to web version exclusive features (e.g., internet, plugins)
- ✅ Usually lower cost, some providers offer discounts
- ✅ Simple development, consistent with standard API interface
Disadvantages:
- ❌ No stability guarantee: Official updates may cause failures
- ❌ May violate terms of service: Risk of account suspension
- ❌ Not suitable for production environments: Only recommended for learning and experimentation
- ❌ Functionality may be incomplete, some advanced features not supported
Use Cases: Learning and experimentation, technical validation, non-critical applications, not recommended for production environments.
⚠️ Important Reminder: Although reverse engineered APIs can quickly provide internet functionality experience, stability cannot be guaranteed. The reverse engineered models provided by APIyi (apiyi.com) platform are for learning and testing only. For production environments, Solution 1 (Tool Calling) or Solution 2 (Encapsulated Internet) is strongly recommended.

Solution 4: MCP Protocol (Model Context Protocol)
Technical Principles
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open protocol introduced by Anthropic, designed to standardize the interaction between AI models and external tools (including web search queries).
Core Concepts:
- MCP Server: Server-side providing tool capabilities (such as web search server)
- MCP Client: Client-side invoking tools (AI application)
- Standardized Protocol: Unified tool definition and invocation format
Workflow:
- Deploy MCP Server to provide web search capabilities
- AI application connects to Server through MCP Client
- Model initiates web request, MCP Client forwards to Server
- Server executes search and returns results
- Model generates answer based on results
Technical Implementation Example
# Implementing web search using MCP protocol
# 1. Install MCP tools
# pip install mcp
# 2. Start MCP Server (providing web search tool)
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.server.models import InitializationOptions
import httpx
app = Server("web-search-server")
@app.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools():
return [
{
"name": "web_search",
"description": "Search the internet for real-time information",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
]
@app.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict):
if name == "web_search":
# Call search API (Google, Bing, etc.)
query = arguments["query"]
results = await search_web(query)
return {"content": [{"type": "text", "text": results}]}
# 3. AI application calls through MCP Client
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from anthropic import Anthropic
async with ClientSession(StdioServerParameters(command="python", args=["mcp_server.py"])) as session:
tools = await session.list_tools()
client = Anthropic()
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What are today's tech news?"}],
tools=tools
)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- ✅ Standardized protocol, reusable tools
- ✅ Decouples models and tools, flexible extension
- ✅ Supports multiple tool combinations, not limited to web search
- ✅ Official Anthropic support, deep Claude integration
Disadvantages:
- ❌ Relatively new technology, ecosystem not yet mature
- ❌ Steep learning curve, requires understanding the protocol
- ❌ Requires MCP Server deployment, increases operational costs
- ❌ Currently mainly supports Claude, limited support for other models
Use Cases: Complex enterprise-level applications requiring integration of multiple tools (web search, databases, API calls, etc.), pursuing standardization and scalability.
💡 Technical Outlook: The MCP protocol represents the future direction of AI tool integration. For teams needing to build complex tool chains, in-depth learning of MCP is recommended. The apiyi.com platform plans to launch MCP Server hosting services in Q2 2025 to simplify deployment and operations.
Solution 5: Workflow Orchestration (External Tool Integration)
Technical Principles
Through workflow orchestration tools (such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, Dify, etc.), combine large models with external tools like search engines, databases, and APIs to execute web queries step by step.
Core Components:
- Large Model API: Provides reasoning and generation capabilities
- Search Tools: Google Search API, Bing API, SerpAPI, etc.
- Workflow Engine: Orchestrates tool calling sequence and logic
- Vector Database: Stores and retrieves search results
Workflow:
- User poses a question
- Workflow engine analyzes question and determines execution steps
- Calls search tools to obtain real-time information
- Stores search results in vector database or passes directly
- Large model generates answer based on search results
- Optional: Further retrieval or multi-round search
Technical Implementation Example
Implementing Web Search Using LangChain:
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, Tool
from langchain.agents import AgentType
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
# Initialize search tool
search = DuckDuckGoSearchRun()
# Define tool list
tools = [
Tool(
name="Web Search",
func=search.run,
description="Used to search the internet for real-time information. Use when latest data, news, or fact-checking is needed."
)
]
# Initialize large model
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4-turbo",
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="https://api.apiyi.com/v1" # Call through apiyi platform
)
# Create Agent
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
verbose=True
)
# Execute web search
response = agent.run("What are today's important tech news?")
print(response)
Implementing Web Search Using Dify:
# Dify workflow configuration
workflow:
- name: "User Input"
type: "start"
- name: "Determine if Web Search Needed"
type: "llm"
model: "gpt-4-turbo"
prompt: "Determine if the following question requires real-time information search: {{user_input}}"
- name: "Search Internet"
type: "tool"
tool: "google_search"
condition: "{{需要联网}} == true"
- name: "Generate Final Answer"
type: "llm"
model: "gpt-4-turbo"
prompt: "Answer based on search results: {{search_results}}"
- name: "Output Result"
type: "end"
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- ✅ Highly flexible, customizable complex logic
- ✅ Supports multiple search sources, parallel searching possible
- ✅ Easy to debug and optimize, each step independently testable
- ✅ Rich ecosystem, abundant ready-made tools and templates
Disadvantages:
- ❌ High learning cost, requires mastering workflow tools
- ❌ Increased system complexity, need to maintain multiple components
- ❌ Higher latency, multi-step execution takes longer
- ❌ Potentially higher cost, multiple calls to model and search APIs
Use Cases: Complex AI applications requiring multi-round search, information integration, knowledge graph construction, and other advanced features.
🎯 Best Practice: Workflow orchestration solutions are suitable for building complex AI Agents and RAG systems. Recommended combination: LangChain + apiyi platform, where LangChain provides powerful workflow capabilities and apiyi provides stable model access and cost optimization.
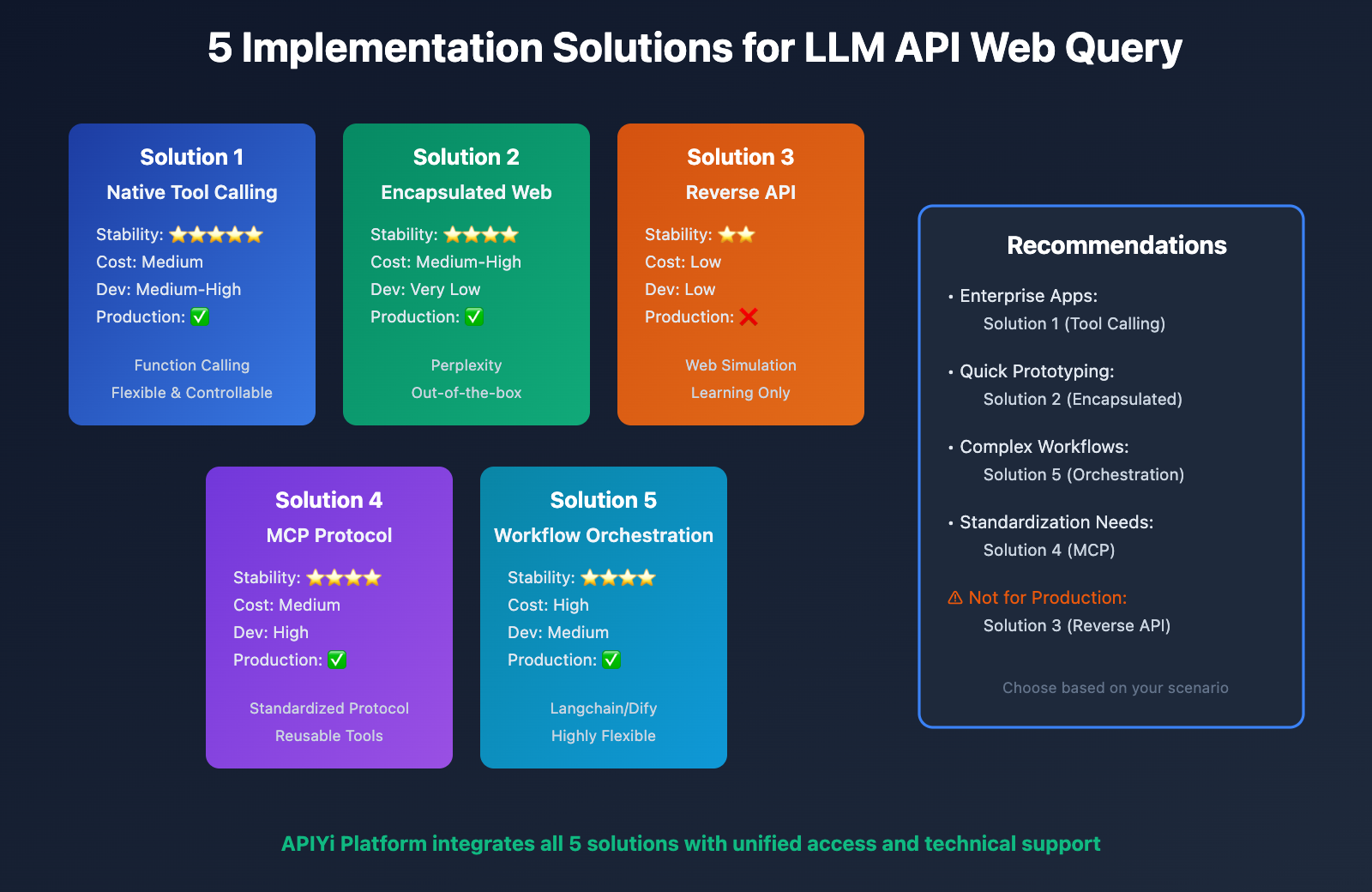
Comprehensive Comparison of 5 Solutions
| Comparison Dimension | Native Tool Calling | Encapsulated Web Access | Reverse API | MCP Protocol | Workflow Orchestration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Development Cost | High | Very Low | Low | Medium-High | Medium |
| Operation Cost | Medium | Low | Low | High | Medium-High |
| Flexibility | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Controllability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Production Ready | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cost Range | Medium | Medium-High | Low | Medium | High |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Gentle | Gentle | Steep | Moderate |
Selection Decision Tree
Do you need highly customized web access logic?
├─ Yes → Do you need to integrate multiple tools?
│ ├─ Yes → Solution 5: Workflow Orchestration (Langchain/Dify)
│ └─ No → Do you pursue standardization?
│ ├─ Yes → Solution 4: MCP Protocol
│ └─ No → Solution 1: Native Tool Calling
└─ No → Can you accept black-box processing?
├─ Yes → Solution 2: Encapsulated Web Access (Perplexity)
└─ No → Is it only for learning and testing?
├─ Yes → Solution 3: Reverse API (use with caution)
└─ No → Re-evaluate requirements, recommend Solution 1 or 2
APIYi Platform Web Access Solutions
Multi-Solution Integration Support
The APIYi platform has integrated the core capabilities of the above 5 solutions:
1. Models Supporting Tool Calling:
- GPT-4 Turbo / GPT-4o (Function Calling)
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet (Tool Use)
- Gemini 1.5 Pro / Gemini 3 Series (Function Calling)
2. Built-in Web Access Models:
- Perplexity Sonar Series
- DeepSeek R1 (partial support)
3. Reverse Web Access Models (for learning only):
- claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-all
- gpt-4-web (select channels)
4. Workflow Tool Integration:
- Compatible with OpenAI SDK, seamlessly integrates with Langchain
- Provides Dify integration documentation and examples
Quick Start in 3 Steps
# 1. Register for APIYi account and obtain API Key
Visit apiyi.com to register, generate API Key in console
# 2. Choose Web Access Solution
# Solution A: Using Tool Calling (GPT-4 Turbo)
curl https://api.apiyi.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What are today'\''s top news headlines?"}],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"description": "Search the internet"
}
}
]
}'
# Solution B: Using Built-in Web Access (Perplexity)
curl https://api.apiyi.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "perplexity-sonar-large",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What are today'\''s top news headlines?"}]
}'
# 3. Process returned results and integrate into application
Cost Optimization Recommendations
1. Choose Solution Based on Scenario:
- Simple queries: Use Perplexity (lower cost)
- Complex logic: Use tool calling + self-built search (high controllability)
2. Batch Query Optimization:
- Use caching mechanism to avoid redundant searches for identical content
- Call multiple search sources in parallel, take fastest result
3. Recharge Bonus:
- APIYi platform recharge bonus promotions, actual cost approximately 20% off
💰 Cost Comparison: Calling Perplexity built-in web access models through the APIYi platform can save approximately 40%-60% in costs compared to self-built tool calling + search API. The platform unified management of multiple models simplifies development and operations.
Best Practices and Selection Recommendations
Scenario 1: News Aggregation and Real-time Updates
Recommended Solution: Wrapped Internet Access (Perplexity) or Workflow Orchestration (Langchain)
Rationale:
- High frequency of news queries, wrapped internet access responds quickly
- Requires source citations, Perplexity automatically provides references
- For multi-source aggregation, use Langchain for parallel searches
Implementation Recommendations:
# Quick implementation using Perplexity
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="perplexity-sonar-large",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Today's tech news"}]
)
Scenario 2: Financial Data Queries and Analysis
Recommended Solution: Native Tool Calling + Professional Financial APIs
Rationale:
- Financial data requires extremely high accuracy
- Requires calling professional financial data sources (Bloomberg, Yahoo Finance)
- Tool calling provides granular control
Implementation Recommendations:
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_stock_price",
"description": "Query real-time stock prices"
}
}
]
# Backend calls Yahoo Finance API or other professional data sources
Scenario 3: Academic Research and Knowledge Retrieval
Recommended Solution: Workflow Orchestration (Langchain + Vector Database)
Rationale:
- Requires multi-source retrieval (Google Scholar, arXiv, PubMed)
- Requires information integration and summary generation
- Vector database supports semantic search
Implementation Recommendations:
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
# 1. Search academic literature
# 2. Vectorize and store
# 3. Semantic retrieval
# 4. Generate summaries with LLM
Scenario 4: Customer Service and Intelligent Q&A
Recommended Solution: Native Tool Calling + Knowledge Base
Rationale:
- Combines internal enterprise knowledge base with external internet access
- Requires precise control over when to access the internet
- Reduces costs by prioritizing internal knowledge
Implementation Recommendations:
# 1. First search internal knowledge base
# 2. If no results, call internet access tool
# 3. Generate answer and store in knowledge base
Frequently Asked Questions
How much additional cost does internet access add?
Tool Calling Solution: Main costs are search APIs (e.g., Google Custom Search API ~$5/1000 queries) + model invocation costs
Wrapped Internet Access: Perplexity ~$0.005-$0.01/query, 20%-50% higher than pure model calls
Workflow Orchestration: Highest cost, including multiple model calls + search APIs, approximately 2-3x pure model costs
How stable are reverse-engineered APIs?
Reverse-engineered API stability cannot be guaranteed:
- Official updates may cause failures at any time
- May trigger anti-scraping mechanisms
- Not recommended for production environments
- Only suitable for learning and technical validation
When can MCP protocol be used at scale?
MCP protocol is currently (early 2025) still in early stages:
- Well supported by Claude
- Limited support from other models
- Ecosystem tools not yet mature
- Expected maturity improvements in second half of 2025
Recommend following Anthropic official documentation and community updates.
How to choose a search API?
| Search API | Characteristics | Cost | Recommended Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Custom Search | High-quality results, comprehensive coverage | $5/1000 queries | General search |
| Bing Search API | Microsoft support, simple integration | $3/1000 queries | Enterprise applications |
| SerpAPI | Aggregates multiple search engines | $50/5000 queries | Multi-source comparison |
| DuckDuckGo | Free, privacy-friendly | Free | Low-cost solutions |
Summary and Action Recommendations
Through this in-depth comparison, we can draw the following core conclusions:
- Native Tool Calling is the Top Choice for Production Environments: High stability and strong controllability, suitable for 80% of enterprise-level applications.
- Encapsulated Internet Access is Ideal for Rapid Prototyping: Services like Perplexity offer out-of-the-box solutions, perfect for startup teams and MVP validation.
- Reverse-Engineered APIs are for Learning Purposes Only: No stability guarantees, not recommended for production environments.
- MCP Protocol Represents the Future Direction: Strong standardization and scalability, though the current ecosystem is not yet mature.
- Workflow Orchestration Suits Complex Applications: Tools like Langchain provide powerful orchestration capabilities, ideal for building AI Agents.
Selection Decision Guide:
- Beginner Developers: Recommended Solution 2 (Encapsulated Internet Access, such as Perplexity)
- Enterprise Applications: Recommended Solution 1 (Native Tool Calling)
- Complex AI Systems: Recommended Solution 5 (Workflow Orchestration)
- Technical Exploration: Consider Solution 4 (MCP Protocol)
- Learning Experience: May try Solution 3 (Reverse-Engineered APIs, use with caution)
Action Recommendations:
- Immediate Experience: Visit API易 apiyi.com to register an account, claim free trial credits, and compare the actual effects of different solutions
- Assess Requirements: Choose the appropriate solution based on application scenarios, budget, and technical capabilities
- Small-Scale Testing: First test in non-critical scenarios to verify stability and costs
- Gradual Migration: Apply to production environments only after maturation
🎯 Final Reminder: Internet search capability is an important enhancement for LLM applications, but you need to choose the right solution based on actual requirements. The API易 apiyi.com platform integrates multiple internet access solutions, providing unified API interfaces and comprehensive technical support, making it the best choice for domestic developers to implement internet search capabilities.